What Is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious and potentially fatal condition that occurs when carbon monoxide (CO) builds up in the bloodstream. This colorless, odorless gas is produced by burning fossil fuels, such as gas, oil, coal, and wood. Because it is undetectable by human senses, it can accumulate in enclosed spaces, leading to dangerous levels without any warning.
When inhaled, carbon monoxide binds with hemoglobin in the blood, forming carboxyhemoglobin. This reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen, leading to symptoms that can range from mild to severe. In some cases, carbon monoxide poisoning can be mistaken for other illnesses, making it crucial to recognize the signs and seek immediate medical attention.
Common Sources of Carbon Monoxide
Understanding where carbon monoxide can come from is essential for prevention. Common sources include:
- Gas-powered appliances (stoves, heaters, water heaters)
- Vehicles running in enclosed spaces (garages)
- Furnaces and boilers
- Charcoal grills and camp stoves
- Wood-burning fireplaces
Who Is at Risk?
While anyone can be affected by carbon monoxide poisoning, certain groups are at higher risk, including:
- Children
- The elderly
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with pre-existing health conditions (e.g., heart disease)
Carbon Monoxide Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning is vital for prompt treatment. Symptoms can vary based on the level of exposure and can often be mistaken for other illnesses, such as the flu or food poisoning. Here are some common symptoms to watch for:
Early Symptoms
- Headache: Often the first sign, it can range from mild to severe.
- Dizziness: A feeling of lightheadedness or unsteadiness.
- Nausea: This can lead to vomiting, which may worsen dehydration.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
Severe Symptoms
If exposure continues, symptoms can escalate to more severe conditions, including:
- Confusion: Difficulty thinking clearly or concentrating.
- Loss of consciousness: In extreme cases, individuals may faint or become unresponsive.
- Chest pain: This can be particularly concerning for those with heart conditions.
- Seizures: A sign of severe poisoning that requires immediate medical attention.
Delayed Symptoms
It’s important to note that some individuals may experience delayed symptoms after initial exposure. These can occur hours or even days later, making it essential to seek medical advice if you suspect carbon monoxide exposure, even if symptoms seem to have subsided.
When to Seek Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning, it is crucial to act quickly. Move to fresh air immediately and call emergency services. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term health effects.
For more information on carbon monoxide poisoning and its treatment, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for evidence-based health answers.
In conclusion, understanding carbon monoxide poisoning is essential for prevention and timely treatment. By being aware of the symptoms and sources of this dangerous gas, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from its harmful effects. Stay safe! 🚨

Risk Factors for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious health risk that can occur in various environments, often without warning. Understanding the risk factors associated with carbon monoxide poisoning is crucial for prevention. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Household Appliances
Many household appliances can produce carbon monoxide if they are not functioning properly. These include:
- Gas stoves and ovens
- Furnaces
- Water heaters
- Fireplaces
Regular maintenance and inspections of these appliances can significantly reduce the risk of carbon monoxide buildup in your home.
2. Poor Ventilation
Inadequate ventilation in enclosed spaces can lead to a dangerous accumulation of carbon monoxide. This is particularly common in:
- Garages (especially when running vehicles)
- Basements
- Small rooms with gas appliances
Ensuring proper airflow and ventilation can help mitigate this risk.
3. Location and Environment
Living in certain environments can increase your risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. For example:
- Urban areas with heavy traffic
- Homes near industrial sites
- Areas with frequent power outages that rely on generators
Being aware of your surroundings and the potential sources of carbon monoxide can help you take necessary precautions.
4. Age and Health Conditions
Some individuals are more vulnerable to the effects of carbon monoxide. These include:
- Children and infants
- Elderly individuals
- People with pre-existing health conditions, such as heart disease or respiratory issues
These groups may experience more severe symptoms and complications from carbon monoxide exposure.
5. Seasonal Risks
Carbon monoxide poisoning incidents often spike during the winter months when heating systems are in use. Be particularly vigilant during:
- Cold weather when heating systems are running
- Power outages that lead to the use of generators indoors
Taking extra precautions during these times can help protect you and your loved ones.
How Carbon Monoxide Affects the Body
Understanding how carbon monoxide affects the body is essential for recognizing the signs of poisoning and seeking timely treatment. Carbon monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas that can lead to serious health issues when inhaled.
1. Mechanism of Action
When carbon monoxide is inhaled, it binds to hemoglobin in the blood more effectively than oxygen does. This reduces the blood’s ability to carry oxygen to vital organs and tissues, leading to hypoxia (lack of oxygen). The effects can be devastating, as every cell in the body requires oxygen to function properly.
2. Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
The symptoms of carbon monoxide poisoning can vary widely and may be mistaken for other illnesses. Common symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion
In severe cases, symptoms can escalate to loss of consciousness and even death. It’s crucial to recognize these signs early, especially in high-risk environments.
3. Delayed Symptoms
One of the most concerning aspects of carbon monoxide poisoning is the potential for delayed symptoms. Individuals may feel fine initially, only to experience symptoms hours later. This delay can lead to a false sense of security, making it vital to remain vigilant if exposure is suspected.
4. Long-term Effects
Even after recovery from carbon monoxide poisoning, some individuals may experience long-term effects, including:
- Cognitive impairments
- Memory issues
- Neurological problems
These effects can significantly impact quality of life, underscoring the importance of prevention and prompt treatment.
In conclusion, being aware of the risk factors and understanding how carbon monoxide affects the body can empower individuals to take proactive measures against this silent threat. Stay safe and informed! 🚨

Diagnosis of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning is a serious health concern that can lead to severe complications or even death if not diagnosed and treated promptly. Understanding how this condition is diagnosed is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing carbon monoxide poisoning is recognizing its symptoms. These can often be mistaken for other illnesses, which can delay treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Headache – Often described as a dull ache, it can be one of the first signs.
- Dizziness – A feeling of lightheadedness or vertigo may occur.
- Nausea and Vomiting – Gastrointestinal symptoms can mimic other conditions.
- Shortness of Breath – Difficulty breathing, especially during exertion.
- Confusion – Cognitive impairment or altered mental status can develop.
- Loss of Consciousness – In severe cases, individuals may faint or become unresponsive.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity and may not appear immediately after exposure. In some cases, delayed symptoms can occur, making it essential to seek medical attention if carbon monoxide exposure is suspected.
Medical Evaluation
If carbon monoxide poisoning is suspected, a healthcare provider will conduct a thorough medical evaluation. This typically includes:
- Patient History – Discussing potential exposure sources, such as faulty heating systems, car exhaust, or gas appliances.
- Physical Examination – Checking for signs of distress, neurological symptoms, and overall health.
- Blood Tests – A blood test can measure the level of carboxyhemoglobin, which indicates the amount of carbon monoxide in the bloodstream.
In some cases, imaging tests like a CT scan may be performed to assess any potential brain damage caused by prolonged exposure. Early diagnosis is critical, as it can significantly improve outcomes.
Treatment Options for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Once diagnosed, prompt treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning is essential to prevent serious health complications. The treatment approach may vary depending on the severity of the poisoning.
Immediate Actions
The first step in treatment is to remove the individual from the source of carbon monoxide exposure. This may involve:
- Evacuation – Moving the person to fresh air immediately.
- Oxygen Therapy – Administering supplemental oxygen to help displace carbon monoxide from the bloodstream.
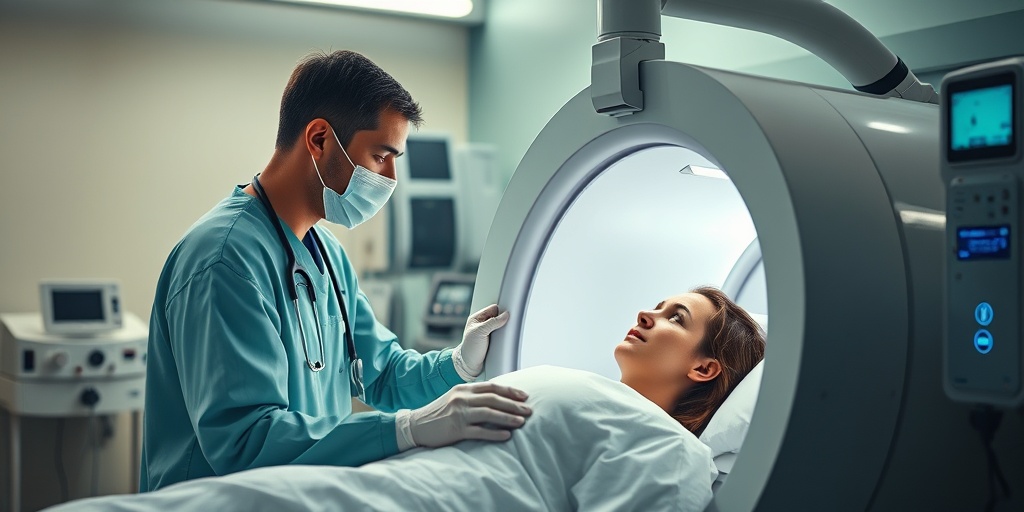
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
In cases of severe carbon monoxide poisoning, hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be recommended. This treatment involves placing the patient in a hyperbaric chamber where they breathe 100% oxygen at increased atmospheric pressure. This method can:
- Accelerate the elimination of carbon monoxide from the body.
- Reduce the risk of long-term neurological damage.
- Improve overall recovery outcomes.
Supportive Care
In addition to oxygen therapy, supportive care may be necessary. This can include:
- Monitoring Vital Signs – Keeping track of heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Fluid Management – Administering intravenous fluids if dehydration or shock is present.
- Neurological Assessment – Regular evaluations to monitor cognitive function and recovery.
Recovery from carbon monoxide poisoning can vary. Some individuals may experience lingering effects, while others may fully recover with prompt treatment. It’s crucial to follow up with healthcare providers for ongoing assessments and support.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for carbon monoxide poisoning can save lives. If you suspect exposure, don’t hesitate to seek medical help immediately! 🚑
Preventing Carbon Monoxide Exposure
Carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning is a serious health risk that can occur in any home or workplace. This colorless, odorless gas is produced by burning fossil fuels, and it can lead to severe health complications or even death if not addressed promptly. Fortunately, there are several effective strategies to prevent carbon monoxide exposure.
1. Install Carbon Monoxide Detectors
One of the most effective ways to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning is to install carbon monoxide detectors in your home. These devices work similarly to smoke detectors and can alert you to dangerous levels of CO in the air. Here are some tips for using them:
- Place detectors on every level of your home, especially near sleeping areas.
- Test the alarms monthly to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Replace batteries at least once a year, or as needed.
- Replace the entire unit every 5-7 years, depending on the manufacturer’s recommendations.
2. Ensure Proper Ventilation
Proper ventilation is crucial in preventing carbon monoxide buildup. Here are some steps you can take:
- Ensure that all fuel-burning appliances, such as furnaces, water heaters, and stoves, are properly vented to the outside.
- Never use a gas stove or oven for heating your home.
- Keep vents and chimneys clear of debris and ensure they are regularly inspected.
3. Regular Maintenance of Appliances
Regular maintenance of your fuel-burning appliances can significantly reduce the risk of carbon monoxide exposure. Consider the following:
- Schedule annual inspections for your heating system, water heater, and any other gas appliances.
- Look for signs of malfunction, such as yellow or orange flames instead of blue, which can indicate incomplete combustion.
- Address any repairs immediately to prevent CO leaks.
4. Be Cautious with Generators and Heaters
During power outages or cold weather, many people turn to generators or space heaters. However, these can be sources of carbon monoxide if not used correctly:
- Always use generators outdoors and away from windows and doors.
- Never use charcoal grills or gas-powered equipment indoors.
- Ensure that any space heaters are vented properly and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
5. Educate Your Family
Education is key in preventing carbon monoxide poisoning. Make sure everyone in your household understands the dangers of CO and knows how to recognize the symptoms of poisoning. Discuss the importance of the following:
- Recognizing the signs of carbon monoxide poisoning, such as headaches, dizziness, and confusion.
- Understanding the importance of evacuating the home immediately if a CO alarm goes off.
- Knowing how to call for help in case of an emergency.
What to Do in Case of Poisoning
If you suspect that you or someone else has been exposed to carbon monoxide, it’s crucial to act quickly. Here’s what you should do:
1. Recognize the Symptoms
Carbon monoxide poisoning symptoms can vary but often include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion or disorientation
In severe cases, symptoms can escalate to loss of consciousness or even death. If you notice these signs, take immediate action!
2. Evacuate the Area
Get everyone out of the building as quickly as possible. Open windows and doors to ventilate the area if it is safe to do so. Ensure that pets are also evacuated. 🚪🐾
3. Call for Emergency Help
Once you are safely outside, call emergency services. Inform them that you suspect carbon monoxide poisoning. If possible, provide them with information about the situation, including the number of people affected and any symptoms they are experiencing.
4. Seek Medical Attention
Even if symptoms seem mild, it’s essential to seek medical attention. Carbon monoxide can cause long-term health effects, and medical professionals can provide the necessary treatment, which may include:
- Administering oxygen therapy to help remove CO from the bloodstream.
- Monitoring for any delayed symptoms that may arise.
5. Follow Up
After treatment, follow up with your healthcare provider to discuss any lingering symptoms or concerns. It’s also a good idea to have your home inspected for potential sources of carbon monoxide to prevent future incidents.
By taking these precautions and knowing how to respond in case of poisoning, you can protect yourself and your loved ones from the dangers of carbon monoxide. Stay safe! 🛡️

Frequently Asked Questions about Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
What is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
Carbon monoxide poisoning occurs when carbon monoxide (CO) gas builds up in the bloodstream, preventing oxygen from entering the body’s cells and tissues. This can lead to serious health issues and even death if not treated promptly.
What are the Symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
Common carbon monoxide poisoning symptoms include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Confusion
- Shortness of breath
In severe cases, symptoms can escalate to loss of consciousness or even death. It’s crucial to seek medical attention if you suspect poisoning.
How is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Treated?
The primary treatment for carbon monoxide poisoning treatment involves administering oxygen. This can be done through:
- Standard oxygen therapy
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in severe cases
These treatments help to remove carbon monoxide from the bloodstream and restore normal oxygen levels.
What Causes Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
Carbon monoxide poisoning causes typically include:
- Faulty gas appliances
- Blocked chimneys
- Running vehicles in enclosed spaces
- Improperly ventilated heating systems
Understanding these causes can help prevent exposure to this dangerous gas.
Can Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Have Delayed Symptoms?
Yes, carbon monoxide poisoning delayed symptoms can occur. Some individuals may not experience symptoms until hours after exposure, making it essential to be aware of the signs and seek help if you suspect poisoning.
Is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning Mistakenly Identified as Other Conditions?
Yes, carbon monoxide poisoning is sometimes mistakenly identified as flu or food poisoning due to overlapping symptoms like headache and nausea. Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
What are the Signs of Severe Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
Severe carbon monoxide poisoning signs may include:
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Severe confusion or disorientation
If you observe these signs, it is vital to call emergency services immediately.
What is the ICD-10 Code for Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
The carbon monoxide poisoning ICD 10 code is T58. This code is used for medical billing and documentation purposes.
How Can I Prevent Carbon Monoxide Poisoning?
To prevent carbon monoxide poisoning, consider the following safety tips:
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home.
- Ensure proper ventilation for gas appliances.
- Have heating systems and chimneys inspected regularly.
- Avoid running vehicles in enclosed spaces.
Taking these precautions can significantly reduce the risk of exposure to carbon monoxide.




