What Is Pica?
Pica is a fascinating yet concerning eating disorder characterized by the persistent consumption of non-nutritive substances. This condition can manifest in various forms, with individuals craving items that are not typically considered food. These can include anything from dirt and clay to chalk, paper, and even hair. While it may seem unusual, pica is a serious condition that can lead to significant health issues if left untreated.
Understanding the Causes of Pica
The exact causes of pica are not entirely understood, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Some studies suggest that deficiencies in essential nutrients, such as iron or zinc, may trigger cravings for non-food items.
- Psychological Factors: Pica is often associated with mental health disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), autism spectrum disorders, and developmental disabilities.
- Environmental Influences: Cultural practices and environmental factors can also play a role. In some cultures, the consumption of certain non-food items is normalized.
Understanding these underlying causes is crucial for effective treatment and management of pica. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of this disorder, it’s essential to seek professional help.
Pica Symptoms
The symptoms of pica can vary widely depending on the individual and the specific non-food items they consume. However, there are some common signs to look out for:
Common Symptoms of Pica
- Cravings for Non-Food Items: A strong desire to eat substances like dirt, clay, chalk, or paper.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Consuming non-food items can lead to digestive problems, including constipation, blockages, or even perforations in severe cases.
- Dental Problems: Chewing on hard substances can cause damage to teeth and gums.
- Weight Loss or Nutritional Deficiencies: Individuals with pica may experience weight loss or deficiencies due to the lack of proper nutrition.
- Behavioral Changes: In some cases, individuals may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased irritability or withdrawal from social interactions.
When to Seek Help
If you notice these symptoms in yourself or someone else, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. Early intervention can help prevent serious health complications associated with pica. A healthcare provider can conduct a thorough evaluation, including physical exams and psychological assessments, to determine the best course of action.
Conclusion
Pica is a complex disorder that requires understanding and compassion. By recognizing the symptoms and underlying causes, individuals can seek the appropriate help and support. For more evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI, a valuable resource for those seeking information on various health topics.
Remember, if you or someone you know is struggling with pica, you are not alone, and help is available. 🌟
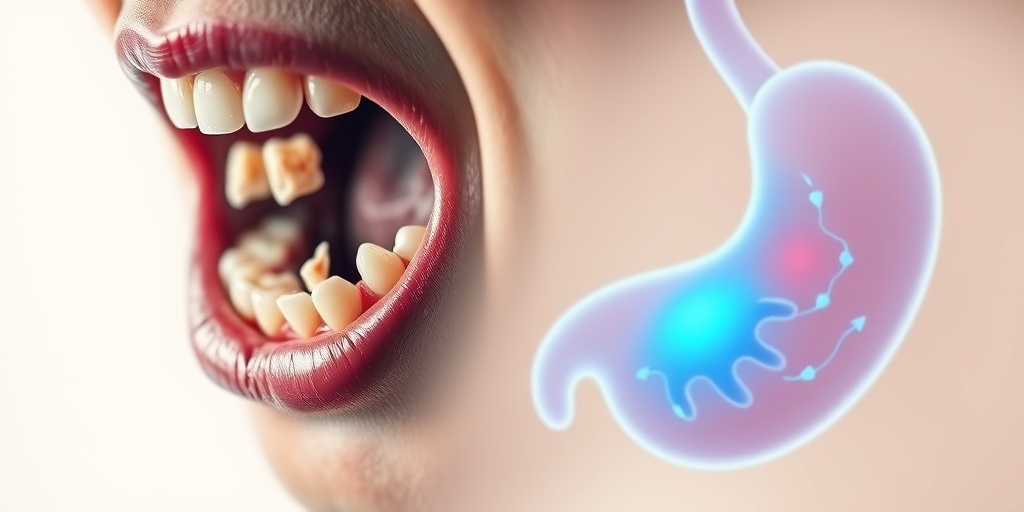
Pica Causes
Pica is a complex eating disorder characterized by the persistent consumption of non-nutritive substances. Understanding the causes of pica is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment. While the exact reasons behind this behavior can vary widely among individuals, several key factors have been identified.
1. Nutritional Deficiencies
One of the most common causes of pica is nutritional deficiencies. Individuals, particularly children and pregnant women, may crave non-food items as a way to compensate for a lack of essential nutrients. For instance:
- Iron deficiency: This is often linked to cravings for dirt or clay, a condition known as geophagia.
- Zinc deficiency: Some individuals may develop a craving for non-food items like paper or chalk.
2. Psychological Factors
Psychological issues can also play a significant role in the development of pica. Conditions such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), autism spectrum disorders, and developmental disabilities may lead to pica behaviors. In these cases, the consumption of non-food items can serve as a coping mechanism or a way to manage anxiety.
3. Cultural Influences
In some cultures, the consumption of certain non-food items is considered a traditional practice. For example, eating clay or chalk may be seen as a remedy for digestive issues or a way to enhance health. This cultural aspect can contribute to the prevalence of pica in specific communities.
4. Stress and Trauma
Experiencing significant stress or trauma can trigger pica behaviors in some individuals. This can include emotional distress from events such as:
- Loss of a loved one
- Abuse or neglect
- Major life changes
In these situations, consuming non-food items may provide a temporary sense of relief or distraction.
5. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also lead to pica. For instance, individuals with intellectual disabilities or those undergoing treatment for mental health disorders may exhibit pica behaviors. Additionally, some gastrointestinal disorders can create cravings for non-food substances as the body attempts to cope with discomfort.
Pica Risk Factors
Identifying the risk factors for pica can help in early detection and intervention. While pica can affect anyone, certain groups are more susceptible to developing this disorder.
1. Age
Pica is most commonly observed in children, particularly those aged 1 to 6 years. Young children are naturally curious and may explore their environment by putting non-food items in their mouths. However, pica can also occur in adults, especially those with underlying health or psychological issues.
2. Gender
Research indicates that pica is more prevalent in females than in males. This may be linked to higher rates of pregnancy-related cravings or nutritional deficiencies among women.
3. Socioeconomic Status
Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may be at a higher risk for pica due to limited access to nutritious food. Inadequate diets can lead to deficiencies that trigger cravings for non-food items.
4. Mental Health Disorders
People with certain mental health disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disabilities, or obsessive-compulsive disorder, are at an increased risk of developing pica. These conditions can affect impulse control and lead to unusual eating behaviors.
5. Pregnancy
Pregnant women are particularly vulnerable to pica, often due to hormonal changes and increased nutritional needs. Cravings for non-food items can arise as the body seeks to fulfill these needs, making it crucial for expectant mothers to maintain a balanced diet.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and risk factors associated with pica is vital for addressing this disorder effectively. By recognizing the underlying issues, individuals can seek appropriate help and support to manage their cravings and improve their overall health. 🌱
Pica Diagnosis
Pica is a complex eating disorder characterized by the persistent consumption of non-nutritive substances, such as dirt, clay, chalk, or even paper. Diagnosing pica can be challenging, as it often overlaps with other medical or psychological conditions. Here’s a closer look at how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition.
Understanding the Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing pica is recognizing its symptoms. Individuals with pica may exhibit:
- Cravings for non-food items: This can include a wide range of substances, from dirt and clay to more unusual items like hair or paint.
- Frequent eating of these substances: The behavior must persist for at least one month and be inappropriate for the developmental level of the individual.
- Negative health effects: Consuming non-food items can lead to gastrointestinal issues, poisoning, or nutritional deficiencies.
Medical Evaluation
If you or someone you know is exhibiting signs of pica, it’s essential to seek a medical evaluation. A healthcare provider will typically:
- Conduct a physical examination: This helps assess any immediate health concerns related to the consumption of non-food items.
- Review medical history: Understanding past health issues, nutritional status, and any psychological conditions is crucial.
- Order laboratory tests: Blood tests may be necessary to check for nutritional deficiencies or other health problems.
Psychological Assessment
Since pica can be linked to psychological conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), or developmental delays, a mental health evaluation may also be recommended. This assessment can help identify any underlying issues that may be contributing to the behavior.
Pica Treatment Options
Treating pica involves a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the disorder. Here are some common treatment options:
Behavioral Therapy
One of the most effective treatments for pica is behavioral therapy. This approach focuses on:
- Identifying triggers: Understanding what prompts the urge to consume non-food items can help in developing coping strategies.
- Positive reinforcement: Encouraging healthy eating habits and rewarding progress can motivate individuals to change their behavior.
Nutritional Counseling
Since pica can lead to nutritional deficiencies, working with a nutritionist can be beneficial. A nutritionist can help:
- Develop a balanced diet: Ensuring that the individual receives adequate nutrients can reduce cravings for non-food items.
- Monitor health: Regular check-ups can help track any health issues arising from pica.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address underlying psychological conditions. This can include:
- Antidepressants: These may help if pica is linked to anxiety or depression.
- Antipsychotics: In severe cases, these medications can help manage symptoms associated with more complex psychological disorders.
Support Groups
Joining a support group can provide individuals and their families with a sense of community and understanding. Sharing experiences and coping strategies can be incredibly beneficial in managing pica.
In conclusion, diagnosing and treating pica requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical evaluation, psychological assessment, and tailored treatment plans. If you suspect that you or someone you know may be struggling with pica, it’s important to seek professional help. Remember, you are not alone, and support is available! 🌟

Pica Complications
Pica is a complex eating disorder characterized by the persistent consumption of non-nutritive substances, such as dirt, clay, chalk, or even paper. While it may seem harmless at first glance, pica can lead to serious health complications that can affect both physical and mental well-being. Understanding these complications is crucial for anyone dealing with this condition or caring for someone who is.
Physical Health Risks
The physical health risks associated with pica can be severe and varied. Here are some of the most common complications:
- Intestinal Blockages: Consuming non-food items can lead to blockages in the digestive tract, which may require surgical intervention.
- Poisoning: Many non-food substances can be toxic. For example, eating lead-based paint chips can lead to lead poisoning, which has serious neurological consequences.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Individuals with pica may neglect their nutritional needs, leading to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
- Dental Issues: Chewing on hard substances can damage teeth and gums, leading to pain and potential tooth loss.
Mental Health Implications
Pica is often associated with underlying mental health issues, which can complicate the condition further. Some potential mental health implications include:
- Increased Anxiety and Depression: The stress of managing pica can exacerbate feelings of anxiety and depression, creating a vicious cycle.
- Social Isolation: Individuals may feel embarrassed about their eating habits, leading to withdrawal from social situations.
- Co-occurring Disorders: Pica is often linked with other disorders, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or autism spectrum disorders, which can complicate treatment.
Long-term Consequences
If left untreated, pica can lead to long-term health issues that may affect quality of life. Chronic health problems, such as gastrointestinal disorders or severe nutritional deficiencies, can arise, necessitating ongoing medical care. Additionally, the psychological toll of living with pica can lead to persistent mental health challenges.
Pica Prevention Strategies
Preventing pica involves a multifaceted approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of the disorder. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
Education and Awareness
One of the first steps in preventing pica is increasing awareness about the disorder. Educating individuals, families, and communities about the risks associated with consuming non-food items can help reduce stigma and encourage those affected to seek help.
Addressing Nutritional Needs
Ensuring that individuals receive adequate nutrition is crucial in preventing pica. Here are some tips:
- Balanced Diet: Encourage a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and proteins to meet nutritional needs.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups can help identify and address any nutritional deficiencies early on.
Behavioral Interventions
Behavioral strategies can be effective in managing pica. Consider the following:
- Positive Reinforcement: Rewarding positive eating behaviors can encourage individuals to choose healthy foods over non-nutritive substances.
- Distraction Techniques: Engaging in activities that keep hands and minds busy can help reduce the urge to consume non-food items.
Professional Support
Seeking professional help is often essential for managing pica effectively. This may include:
- Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals understand the underlying causes of their pica and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
- Medical Intervention: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address co-occurring mental health disorders.
By implementing these prevention strategies, individuals and caregivers can work towards reducing the incidence of pica and its associated complications. Remember, early intervention is key to managing this complex disorder effectively! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Pica
What is Pica?
Pica is a psychological disorder characterized by the persistent consumption of non-nutritive substances. This can include items such as dirt, clay, chalk, or even paper. It is often associated with nutritional deficiencies or mental health conditions.
What causes Pica?
The exact cause of Pica is not fully understood, but it can be linked to various factors, including:
- Nutritional deficiencies, particularly iron or zinc
- Mental health disorders, such as autism or obsessive-compulsive disorder
- Stress or trauma
- Pregnancy-related cravings
Who is most at risk for developing Pica?
While anyone can develop Pica, certain groups are more at risk, including:
- Children, especially those with developmental disorders
- Pregnant women
- Individuals with mental health issues
How is Pica diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Pica typically involves a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional, which may include:
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Psychological assessment
What are the potential health risks associated with Pica?
Engaging in Pica can lead to various health complications, such as:
- Intestinal blockages
- Infections
- Poisoning from toxic substances
How can Pica be treated?
Treatment for Pica often involves a combination of approaches, including:
- Addressing any underlying nutritional deficiencies
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Medication for associated mental health conditions
Can Pica be prevented?
While not all cases of Pica can be prevented, some strategies may help reduce the risk, such as:
- Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients
- Providing support for individuals with mental health issues
- Encouraging healthy coping mechanisms for stress
When should I seek help for Pica?
If you or someone you know is exhibiting signs of Pica, it is important to seek help from a healthcare professional, especially if the behavior is persistent or causing health issues. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes. 🌟




