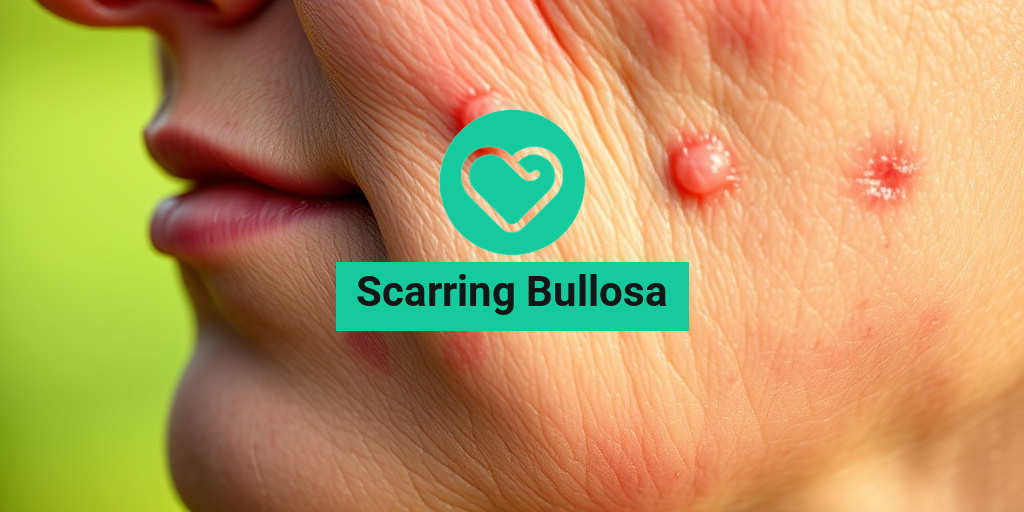
What Is Scarring Bullosa?
Scarring Bullosa is a rare genetic skin disorder that falls under the umbrella of epidermolysis bullosa (EB). This condition is characterized by the formation of blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, which can lead to significant scarring over time. The blisters typically arise from minor friction or trauma, making everyday activities challenging for those affected.
The underlying cause of Scarring Bullosa is a defect in the genes responsible for producing proteins that help anchor the layers of skin together. When these proteins are absent or dysfunctional, the skin becomes fragile and prone to blistering. While there are several types of epidermolysis bullosa, Scarring Bullosa is particularly noted for its tendency to cause extensive scarring as the blisters heal.
Types of Epidermolysis Bullosa
Understanding the different types of epidermolysis bullosa can help clarify the specific characteristics of Scarring Bullosa:
- Simplex EB: The mildest form, usually affecting only the outer layer of skin.
- Dystrophic EB: Involves deeper layers of skin and is often associated with scarring.
- Junctional EB: A more severe form that affects the junction between the outer and inner layers of skin.
- Scarring Bullosa: A subtype of dystrophic EB, known for its significant scarring and blistering.
Individuals with Scarring Bullosa may experience varying degrees of severity, with some facing more challenges than others. The condition can significantly impact quality of life, leading to physical discomfort and emotional distress.
Scarring Bullosa Symptoms
The symptoms of Scarring Bullosa can vary widely among individuals, but there are some common signs to look out for:
1. Blister Formation
The hallmark of Scarring Bullosa is the formation of blisters on the skin. These blisters can appear spontaneously or as a result of minor trauma, such as friction from clothing or even gentle touch. The blisters may be filled with clear fluid and can be painful.
2. Scarring
As the blisters heal, they often leave behind scars that can be disfiguring. The scarring can be extensive, leading to changes in skin texture and color. Over time, these scars can become thickened and may limit mobility if they occur over joints.
3. Skin Fragility
Individuals with Scarring Bullosa often have skin that is extremely fragile. This fragility means that even minor injuries can lead to new blisters, creating a cycle of damage and healing that can be difficult to manage.
4. Pain and Discomfort
The presence of blisters and scars can lead to significant pain and discomfort. This can affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Managing pain is an essential aspect of care for those with Scarring Bullosa.
5. Risk of Infection
Open blisters can increase the risk of infection. It’s crucial for individuals with Scarring Bullosa to maintain proper wound care and hygiene to minimize this risk. Infections can complicate healing and lead to further scarring.
6. Emotional Impact
The visible nature of Scarring Bullosa can also have an emotional toll. Many individuals may experience feelings of self-consciousness or anxiety due to their skin condition. Support from healthcare providers, family, and support groups can be invaluable in managing these feelings.
If you or someone you know is dealing with Scarring Bullosa, it’s essential to seek guidance from healthcare professionals who specialize in skin disorders. Resources like Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) can provide evidence-based answers and support for managing this condition effectively.
In conclusion, Scarring Bullosa is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to care. Understanding the symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment can help individuals lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this disorder. 🌟

Causes of Scarring Bullosa
Scarring Bullosa, often associated with a group of genetic disorders known as Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB), is primarily characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily. Understanding the causes of this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment. Let’s delve into the underlying factors that contribute to Scarring Bullosa.
Genetic Mutations
The primary cause of Scarring Bullosa is genetic mutations that affect the proteins responsible for skin integrity. These mutations can occur in various genes, leading to different forms of EB. The most common types include:
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB): Caused by mutations in the COL7A1 gene, which encodes type VII collagen, essential for anchoring the epidermis to the dermis.
- Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB): Linked to mutations in genes that produce proteins crucial for the adhesion of the epidermis to the dermis.
- Simplex Epidermolysis Bullosa (SEB): Resulting from mutations in keratin genes, leading to skin fragility.
These genetic defects disrupt the normal structure and function of the skin, making it more susceptible to injury and blister formation. When these blisters heal, they can lead to scarring, hence the term “Scarring Bullosa.” 🩹
Environmental Factors
While genetic mutations are the primary cause, certain environmental factors can exacerbate the condition. These include:
- Friction and Trauma: Everyday activities such as walking, playing, or even wearing clothes can cause friction, leading to blister formation.
- Temperature Changes: Extreme heat or cold can affect skin integrity, making it more prone to blistering.
- Infections: Skin infections can complicate the healing process, leading to increased scarring.
Being aware of these environmental triggers can help individuals with Scarring Bullosa take preventive measures to protect their skin. 🌞
Risk Factors for Scarring Bullosa
Understanding the risk factors associated with Scarring Bullosa is essential for early diagnosis and management. While the condition is primarily genetic, several factors can influence its severity and the likelihood of developing complications.
Family History
One of the most significant risk factors for Scarring Bullosa is a family history of the condition. Since EB is inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, individuals with a parent or sibling affected by the disorder are at a higher risk of developing it themselves. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families with a history of EB. 🧬
Age and Gender
Scarring Bullosa can affect individuals of any age, but it is often diagnosed in infancy or early childhood. Some studies suggest that males may be more frequently affected than females, although this can vary depending on the specific type of EB. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with certain underlying health conditions may be at an increased risk for developing more severe forms of Scarring Bullosa. These conditions can include:
- Immunodeficiency Disorders: A weakened immune system can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, complicating the healing process.
- Other Skin Disorders: Conditions that affect skin integrity can exacerbate the symptoms of Scarring Bullosa.
Managing these underlying health issues can play a significant role in improving the quality of life for those affected by Scarring Bullosa. 🏥
Socioeconomic Factors
Access to healthcare and resources can also influence the management of Scarring Bullosa. Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face challenges in obtaining necessary treatments, leading to worse outcomes. Awareness and education about the condition can empower families to seek appropriate care and support.
In summary, while the primary cause of Scarring Bullosa is genetic, various risk factors can influence its severity and management. Understanding these factors is vital for individuals and families affected by this condition, enabling them to take proactive steps in their care journey. 🌈

Diagnosis of Scarring Bullosa
Diagnosing Scarring Bullosa, particularly its most common form, epidermolysis bullosa (EB), can be a complex process. This condition is characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily, leading to scarring over time. Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing scarring bullosa typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation. A healthcare provider will assess the patient’s medical history and conduct a physical examination. Key aspects they will look for include:
- Blistering Patterns: The presence of blisters, their location, and frequency can provide significant clues.
- Family History: Since some forms of EB are inherited, a family history of similar skin conditions may be relevant.
- Age of Onset: The age at which symptoms first appear can help differentiate between various types of EB.
Laboratory Tests
In addition to a clinical evaluation, laboratory tests are often necessary to confirm the diagnosis of scarring bullosa. These may include:
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample of skin is taken and examined under a microscope to identify the specific type of EB.
- Genetic Testing: This can help identify mutations in genes associated with EB, providing a definitive diagnosis.
- Immunofluorescence Microscopy: This test helps visualize the proteins in the skin that are affected by EB.
Early diagnosis is essential for managing symptoms and preventing complications associated with scarring bullosa. If you suspect you or a loved one may have this condition, seeking medical advice promptly is crucial. 🩺
Treatment Options for Scarring Bullosa
While there is currently no cure for scarring bullosa, various treatment options can help manage symptoms, promote healing, and improve the quality of life for those affected. The treatment plan often depends on the severity of the condition and the specific type of EB.
Wound Care Management
Proper wound care is vital for individuals with scarring bullosa. This includes:
- Gentle Cleansing: Keeping the affected areas clean to prevent infection is essential.
- Moisturizing: Using emollients can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce friction.
- Dressings: Specialized dressings can protect blisters and promote healing.
Pain Management
Pain is a common symptom associated with scarring bullosa. Effective pain management strategies may include:
- Topical Analgesics: Creams or ointments that numb the skin can provide relief.
- Oral Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may be necessary for more severe pain.
Preventive Measures
Preventing blisters and skin damage is a key aspect of managing scarring bullosa. Some preventive measures include:
- Avoiding Friction: Wearing loose-fitting clothing can help minimize skin irritation.
- Protective Gear: Using padding or protective gear during activities can prevent injuries.
- Sun Protection: Applying sunscreen can help protect sensitive skin from UV damage.
Advanced Treatments
In more severe cases, advanced treatments may be considered, such as:
- Skin Grafting: This surgical procedure can help repair extensive skin damage.
- Gene Therapy: Research is ongoing into gene therapy options that may one day offer a cure for certain types of EB.
Managing scarring bullosa requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s needs. Collaboration with a healthcare team, including dermatologists and wound care specialists, is essential for optimal care. 🌟

Living with Scarring Bullosa
Scarring Bullosa, often associated with epidermolysis bullosa (EB), is a rare genetic skin condition that leads to fragile skin and blister formation. For those living with this condition, daily life can present unique challenges. Understanding these challenges and finding effective coping strategies is essential for improving quality of life.
Understanding Scarring Bullosa
Scarring Bullosa is characterized by the formation of blisters on the skin due to minor trauma or friction. These blisters can be painful and may lead to scarring as they heal. The condition is caused by mutations in genes responsible for skin integrity, resulting in a lack of adhesion between the layers of the skin.
Daily Challenges
Living with Scarring Bullosa can be daunting. Here are some common challenges faced by individuals:
- Skin Fragility: The skin is extremely sensitive, making everyday activities like dressing, bathing, and even walking potentially harmful.
- Blister Management: Frequent blistering requires careful management to prevent infections and minimize scarring.
- Emotional Impact: The visible nature of the condition can lead to feelings of self-consciousness and social anxiety.
Coping Strategies
While living with Scarring Bullosa can be challenging, there are several strategies that can help manage the condition:
- Protective Clothing: Wearing soft, breathable fabrics can reduce friction and protect the skin from injury.
- Moisturizers and Dressings: Regular application of moisturizers and specialized dressings can help keep the skin hydrated and promote healing.
- Support Networks: Connecting with support groups or online communities can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the condition.
Seeking Professional Help
Regular consultations with dermatologists and specialists in wound care are crucial for managing Scarring Bullosa effectively. They can provide tailored treatment plans, including:
- Topical Treatments: Prescription creams and ointments can help manage pain and promote healing.
- Physical Therapy: This can improve mobility and reduce the risk of contractures, which can occur due to scarring.
- Psychological Support: Therapy can help individuals cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
Scarring Bullosa Outlook and Prognosis
The outlook for individuals with Scarring Bullosa varies significantly depending on the severity of the condition and the specific type of EB involved. Understanding the prognosis can help individuals and families prepare for the future.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Several factors can influence the prognosis for someone living with Scarring Bullosa:
- Type of EB: There are different types of epidermolysis bullosa, each with varying degrees of severity. Some types may lead to more significant complications than others.
- Age of Onset: Early diagnosis and intervention can improve outcomes and quality of life.
- Access to Care: Regular medical care and access to specialized treatments can significantly impact the overall health and well-being of individuals with Scarring Bullosa.
Long-Term Health Considerations
Individuals with Scarring Bullosa may face long-term health challenges, including:
- Increased Risk of Skin Cancer: Chronic skin damage can elevate the risk of developing skin cancers, making regular dermatological check-ups essential.
- Infections: Open wounds from blisters can become infected, necessitating vigilant wound care and monitoring.
- Psychosocial Effects: The emotional toll of living with a visible condition can lead to anxiety and depression, highlighting the importance of mental health support.
Living a Full Life
Despite the challenges, many individuals with Scarring Bullosa lead fulfilling lives. With the right support, treatment, and coping strategies, they can pursue their passions and maintain strong relationships. Awareness and education about the condition can also foster understanding and support from the community, making a significant difference in the lives of those affected. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Scarring Bullosa
What is Scarring Bullosa?
Scarring Bullosa refers to a group of genetic skin disorders characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily. This condition is often associated with epidermolysis bullosa (EB), which is caused by defects in the proteins that help anchor the skin layers together.
What causes Scarring Bullosa?
The primary cause of Scarring Bullosa is genetic mutations that affect the skin’s structural proteins. These mutations lead to skin blistering and subsequent scarring as the blisters heal. The condition can be inherited in various patterns, including autosomal dominant and recessive traits.
What are the symptoms of Scarring Bullosa?
- Frequent skin blistering
- Severe pain and discomfort
- Scarring and thickening of the skin
- Increased susceptibility to infections
How is Scarring Bullosa diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough physical examination and a review of the patient’s medical history. Genetic testing may also be conducted to identify specific mutations associated with Scarring Bullosa.
What treatments are available for Scarring Bullosa?
While there is no cure for Scarring Bullosa, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include:
- Wound care and dressing changes
- Pain management
- Antibiotics for infections
- Physical therapy to maintain mobility
Can Scarring Bullosa lead to other health issues?
Yes, individuals with Scarring Bullosa may face additional health challenges, including:
- Increased risk of skin cancer due to chronic skin damage
- Emotional and psychological impacts from living with a chronic condition
- Potential complications from infections
Is there ongoing research for Scarring Bullosa?
Yes, research is ongoing to better understand Scarring Bullosa and to develop new treatments. Advances in gene therapy and wound care are particularly promising areas of study.
Where can I find support for Scarring Bullosa?
Support groups and organizations dedicated to skin disorders can provide valuable resources and community support for individuals and families affected by Scarring Bullosa. Online forums and local support groups can also be beneficial.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Scarring Bullosa?
Yes, certain lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms, such as:
- Maintaining a healthy diet to support skin health
- Avoiding known triggers that may cause blistering
- Practicing good skin hygiene
What should I do if I suspect I have Scarring Bullosa?
If you suspect you or a loved one may have Scarring Bullosa, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan. Early intervention can help improve quality of life.