What Is Guenther Porphyria?
Guenther Porphyria, a rare metabolic disorder, falls under the umbrella of porphyrias, which are a group of conditions caused by the buildup of porphyrins or porphyrin precursors in the body. These compounds are essential for the production of heme, a critical component of hemoglobin that carries oxygen in the blood. When the body lacks the necessary enzymes to break down porphyrins, it can lead to various health issues.
This specific type of porphyria is named after Dr. Guenther, who made significant contributions to the understanding of this condition. Guenther Porphyria primarily affects the skin and nervous system, leading to a range of symptoms that can vary in severity. Understanding this disorder is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Types of Guenther Porphyria
Guenther Porphyria can be classified into different types based on the specific enzyme deficiency involved. The most common types include:
- Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP): Characterized by sudden attacks of abdominal pain, neurological symptoms, and psychiatric issues.
- Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT): Primarily affects the skin, causing blistering and sensitivity to sunlight.
- Hereditary Coproporphyria (HCP): Involves both skin and neurological symptoms, often triggered by certain medications or alcohol.
Each type has its own unique set of challenges, making it essential for individuals to receive a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Guenther Porphyria Symptoms
The symptoms of Guenther Porphyria can be quite diverse, often leading to confusion and misdiagnosis. They can be broadly categorized into two main groups: neurological symptoms and cutaneous symptoms.
Neurological Symptoms
Neurological manifestations are particularly concerning as they can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Common neurological symptoms include:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Often described as cramping or sharp pain, this can be debilitating.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms can accompany abdominal pain and may lead to dehydration.
- Muscle Weakness: Patients may experience weakness in their limbs, making daily activities challenging.
- Psychiatric Symptoms: Anxiety, confusion, and hallucinations can occur, particularly during acute attacks.
Cutaneous Symptoms
For those with cutaneous manifestations, the symptoms can be equally distressing. These include:
- Blistering Skin Lesions: These often appear on sun-exposed areas of the body, such as the face and hands.
- Photosensitivity: Individuals may develop rashes or blisters after exposure to sunlight.
- Hyperpigmentation: Darkening of the skin can occur in areas affected by blistering.
When to Seek Help
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms that may be related to Guenther Porphyria, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis can lead to better management of the condition and improve overall quality of life. Healthcare professionals can conduct specific tests to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
For more information and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI. This resource can provide valuable insights into managing health conditions like Guenther Porphyria.
In conclusion, Guenther Porphyria is a complex disorder that requires a comprehensive understanding of its symptoms and types. By recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate care, individuals can navigate this challenging condition more effectively. 🌟
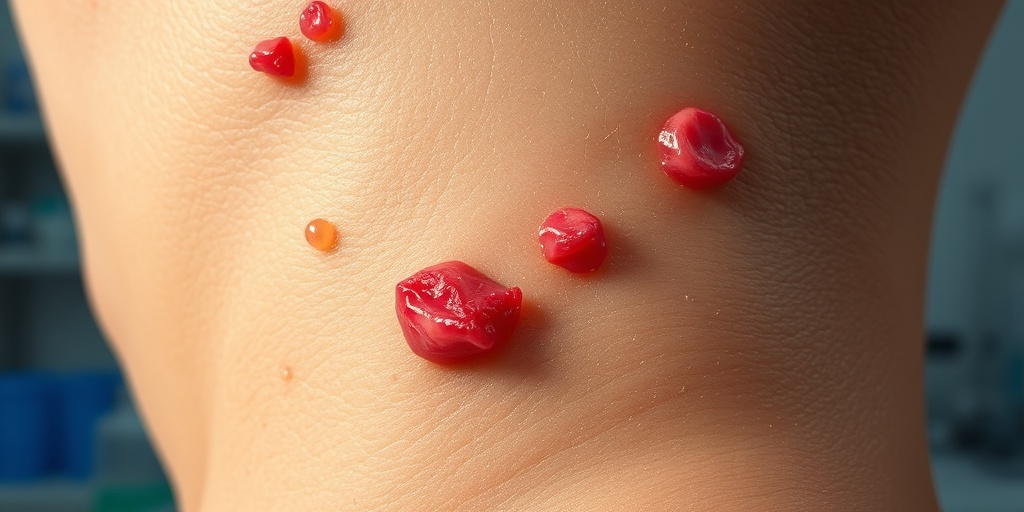
Causes of Guenther Porphyria
Guenther Porphyria, a rare and complex disorder, is part of a group of diseases known as porphyrias. These conditions arise from an imbalance in the production of heme, a vital component of hemoglobin in our blood. Understanding the causes of Guenther Porphyria is essential for diagnosis and management. Let’s delve into the primary causes of this condition.
Genetic Mutations
The primary cause of Guenther Porphyria is genetic mutations. This condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can lead to the disorder in their offspring. The mutations typically occur in the genes responsible for heme production, disrupting the normal metabolic pathway.
Environmental Triggers
While genetic factors play a significant role, certain environmental triggers can exacerbate the symptoms of Guenther Porphyria. These triggers may include:
- Medications: Some drugs can provoke acute attacks in individuals with porphyria. It’s crucial for patients to consult healthcare providers before starting any new medication.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can lead to increased porphyrin levels, worsening symptoms.
- Dietary Factors: A diet low in carbohydrates and high in protein may trigger symptoms in some individuals.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during menstruation, can trigger episodes in women.
Infections and Stress
Infections and significant stress can also act as catalysts for Guenther Porphyria symptoms. The body’s response to stress can lead to increased production of certain hormones, which may further disrupt heme synthesis. Recognizing these triggers is vital for managing the condition effectively.
Risk Factors for Guenther Porphyria
Understanding the risk factors associated with Guenther Porphyria can help in early detection and prevention strategies. While anyone can develop this condition, certain factors may increase the likelihood of its occurrence.
Family History
Having a family history of porphyria significantly increases the risk of developing Guenther Porphyria. If a close relative has been diagnosed with this condition, it’s essential to discuss genetic testing and counseling with a healthcare provider.
Gender and Age
Guenther Porphyria tends to affect women more than men, particularly during their reproductive years. The age of onset can vary, but symptoms often appear between the ages of 20 and 40. Awareness of these demographic factors can aid in recognizing potential cases early.
Previous Medical Conditions
Individuals with a history of certain medical conditions, such as liver disease or hormonal disorders, may be at a higher risk for developing Guenther Porphyria. These conditions can impact the body’s ability to process heme effectively, leading to an increased likelihood of porphyria symptoms.
Exposure to Chemicals
Exposure to specific chemicals, particularly those used in the manufacturing of dyes, pesticides, and solvents, can heighten the risk of developing Guenther Porphyria. Occupational exposure is a significant concern for individuals working in industries where these substances are prevalent.
Other Lifestyle Factors
Several lifestyle factors can also contribute to the risk of Guenther Porphyria, including:
- Smoking: Tobacco use can exacerbate symptoms and increase the risk of complications.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can lead to metabolic changes that may trigger porphyria symptoms.
- High-Stress Lifestyle: Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that may trigger episodes.
By understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Guenther Porphyria, individuals can take proactive steps towards management and prevention. Awareness is key in navigating this complex condition! 🌟

Diagnosing Guenther Porphyria
Diagnosing Guenther Porphyria can be a complex process, as it often mimics other medical conditions. This rare metabolic disorder affects the body’s ability to produce heme, a crucial component of hemoglobin. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management and treatment. Here’s a closer look at the diagnostic process.
Understanding Symptoms
The first step in diagnosing Guenther Porphyria is recognizing its symptoms, which can vary widely among individuals. Common symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain: Often severe and can be accompanied by nausea.
- Skin sensitivity: Sun exposure may lead to blistering and skin damage.
- Neurological issues: These can include confusion, seizures, and muscle weakness.
- Psychiatric symptoms: Anxiety, depression, and hallucinations may occur.
Due to the diverse nature of these symptoms, it’s crucial for patients to provide a comprehensive medical history to their healthcare provider.
Laboratory Tests
Once symptoms are noted, healthcare providers typically recommend a series of laboratory tests to confirm a diagnosis of Guenther Porphyria. These tests may include:
- Urine tests: Elevated levels of porphobilinogen (PBG) in urine can indicate porphyria.
- Blood tests: These can help identify abnormalities in heme production.
- Genetic testing: This can confirm the presence of mutations associated with Guenther Porphyria.
It’s important to note that these tests may need to be repeated during acute attacks, as levels can fluctuate significantly.
Consulting Specialists
Due to the complexity of Guenther Porphyria, patients are often referred to specialists such as hematologists or geneticists. These experts can provide a more in-depth analysis and help tailor a management plan that addresses the specific needs of the patient.
Treatment Options for Guenther Porphyria
While there is currently no cure for Guenther Porphyria, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and reduce the frequency of attacks. The approach to treatment often depends on the severity of the condition and the specific symptoms experienced by the patient.
Managing Acute Attacks
During acute attacks, immediate treatment is crucial. Options include:
- Intravenous (IV) glucose: Administering glucose can help suppress the production of porphyrins.
- Hemin therapy: This involves the administration of heme to help restore balance in heme production.
- Pain management: Analgesics may be prescribed to alleviate severe abdominal pain.
These treatments are typically administered in a hospital setting, especially during severe episodes.
Long-term Management Strategies
For long-term management, patients may consider the following strategies:
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding factors that can precipitate attacks, such as certain medications, alcohol, and stress, is vital.
- Dietary modifications: A balanced diet rich in carbohydrates can help prevent attacks.
- Regular monitoring: Routine check-ups with healthcare providers can help manage the condition effectively.
Additionally, some patients may benefit from counseling or support groups to cope with the psychological aspects of living with a chronic condition.
Emerging Treatments
Research is ongoing in the field of porphyria, and new treatments are being explored. Gene therapy and novel medications are areas of interest that may offer hope for improved management of Guenther Porphyria in the future. Staying informed about advancements in treatment options is essential for patients and their families.
In conclusion, while Guenther Porphyria presents significant challenges, a combination of immediate and long-term treatment strategies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals and adherence to management plans are key to navigating this complex condition. 🌟

Living with Guenther Porphyria
Guenther Porphyria, a rare metabolic disorder, can significantly impact the lives of those diagnosed with it. Understanding how to manage this condition is crucial for maintaining a good quality of life. In this section, we will explore the challenges faced by individuals living with Guenther Porphyria and provide practical tips for coping with the condition.
Understanding Guenther Porphyria
Guenther Porphyria is part of a group of disorders known as porphyrias, which are caused by the buildup of porphyrins in the body. These compounds are essential for the production of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. When the body cannot process porphyrins effectively, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
- Abdominal pain 🤕
- Skin sensitivity to sunlight ☀️
- Nerve pain and weakness
- Psychological symptoms, such as anxiety and confusion
Living with Guenther Porphyria often means navigating these symptoms while also managing the emotional and psychological toll of the condition. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is essential for coping effectively.
Managing Symptoms
While there is no cure for Guenther Porphyria, several strategies can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being:
- Regular medical check-ups: Staying in touch with healthcare providers ensures that any complications are addressed promptly.
- Medication management: Some individuals may benefit from medications that help alleviate symptoms or prevent attacks.
- Dietary adjustments: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support overall health. Some patients find that avoiding certain foods triggers their symptoms.
- Sun protection: Since skin sensitivity is a common issue, using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing can help prevent flare-ups.
- Stress management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which may exacerbate symptoms.
Building a Support Network
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of Guenther Porphyria can be incredibly beneficial. Consider joining support groups, either in-person or online, where you can share experiences, tips, and emotional support. Engaging with a community can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide valuable insights into managing the condition.
Future Research on Guenther Porphyria
The field of porphyria research is evolving, and there is hope for advancements that could improve the lives of those affected by Guenther Porphyria. Ongoing studies aim to deepen our understanding of the disorder and explore new treatment options.
Current Research Trends
Researchers are focusing on several key areas to enhance our understanding of Guenther Porphyria:
- Genetic studies: Understanding the genetic mutations that lead to Guenther Porphyria can help identify at-risk individuals and develop targeted therapies.
- New treatment modalities: Investigating novel medications and therapies that could alleviate symptoms or correct metabolic imbalances is a priority.
- Patient registries: Collecting data from individuals with Guenther Porphyria can help researchers identify patterns and improve treatment protocols.
Potential Breakthroughs
As research progresses, several potential breakthroughs could change the landscape of Guenther Porphyria management:
- Gene therapy: This innovative approach aims to correct the underlying genetic defects, potentially offering a long-term solution for those affected.
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic profiles could lead to more effective management strategies.
- Improved diagnostic tools: Enhanced testing methods may allow for earlier diagnosis and intervention, reducing the severity of symptoms.
Community Involvement and Awareness
Raising awareness about Guenther Porphyria is crucial for fostering research and support. Engaging in community events, participating in awareness campaigns, and sharing personal stories can help bring attention to this rare condition. The more people know about Guenther Porphyria, the more likely it is that funding and resources will be allocated for research and support initiatives.
In conclusion, while living with Guenther Porphyria presents challenges, understanding the condition and staying informed about ongoing research can empower individuals to manage their health effectively. With continued advancements in research and a strong support network, there is hope for a brighter future for those affected by this disorder. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Guenther Porphyria
What is Guenther Porphyria?
Guenther Porphyria is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body’s ability to produce heme, a component of hemoglobin. This condition can lead to a variety of symptoms, including skin sensitivity, abdominal pain, and neurological issues.
What are the symptoms of Guenther Porphyria?
Symptoms can vary widely among individuals but may include:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Skin rashes or blisters
- Neurological symptoms such as confusion or seizures
- Muscle weakness
How is Guenther Porphyria diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Laboratory tests to measure porphyrins in the blood or urine
What treatments are available for Guenther Porphyria?
While there is no cure for Guenther Porphyria, treatments focus on managing symptoms and preventing attacks. Options may include:
- Avoiding triggers such as certain medications and alcohol
- Intravenous heme therapy
- Pain management strategies
Can Guenther Porphyria be inherited?
Yes, Guenther Porphyria is an inherited condition, typically passed down in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means that only one copy of the mutated gene from an affected parent can cause the disorder in their offspring.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help manage Guenther Porphyria?
Individuals with Guenther Porphyria can benefit from certain lifestyle adjustments, such as:
- Maintaining a balanced diet
- Staying hydrated
- Avoiding sun exposure to reduce skin symptoms
Where can I find support for Guenther Porphyria?
Support groups and organizations dedicated to porphyria can provide valuable resources and community support. Online forums and local health organizations can also be helpful in connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with Guenther Porphyria.
Is there ongoing research on Guenther Porphyria?
Yes, research is ongoing to better understand Guenther Porphyria and develop new treatments. Clinical trials may be available for those interested in participating.
What should I do if I suspect I have Guenther Porphyria?
If you suspect you have Guenther Porphyria, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate management strategies. 🩺




