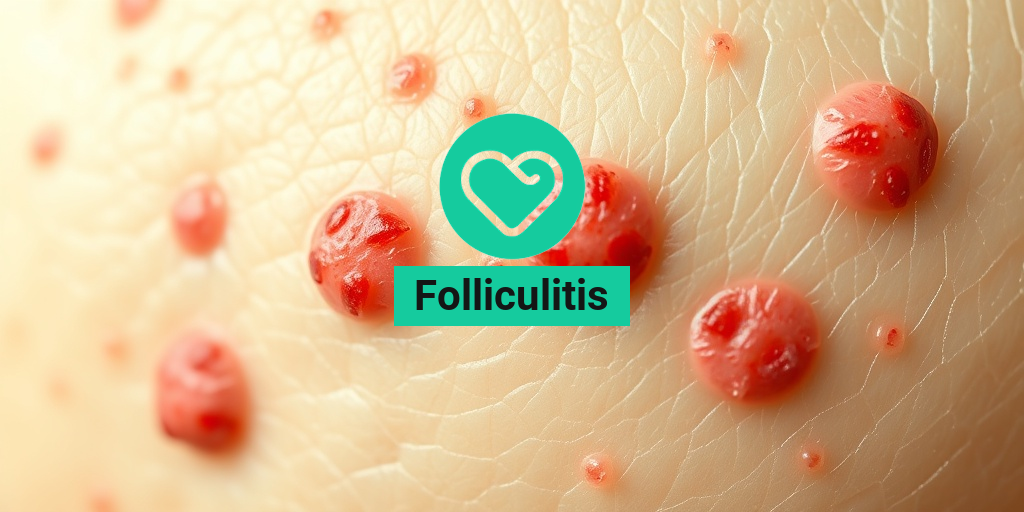
What Is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles. It can occur anywhere on the body where hair grows, including the scalp, face, and even the buttocks. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including bacterial or fungal infections, irritation from shaving, or even certain skin conditions like acne. Understanding folliculitis is essential for effective treatment and prevention.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can be classified into several types, each with its own causes and characteristics:
- Bacterial Folliculitis: This is the most common type, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. It typically appears as small, red bumps or pus-filled blisters.
- Fungal Folliculitis: Caused by yeast or fungi, this type often occurs in warm, moist areas of the body. It can resemble bacterial folliculitis but may require different treatment.
- Folliculitis Decalvans: A more severe form that can lead to hair loss, this type is often chronic and may require specialized treatment.
- Folliculitis Barbae: Commonly known as barber’s itch, this type affects the beard area and is often caused by shaving.
Causes of Folliculitis
Understanding the causes of folliculitis can help in preventing its occurrence. Some common causes include:
- Bacterial Infections: As mentioned, bacteria can infect hair follicles, leading to inflammation.
- Fungal Infections: Yeast infections can also cause folliculitis, particularly in warm and humid conditions.
- Irritation: Shaving, tight clothing, or friction from sports equipment can irritate hair follicles.
- Skin Conditions: Conditions like acne or dermatitis can increase the risk of developing folliculitis.
Folliculitis Symptoms
The symptoms of folliculitis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, some common signs to look out for include:
Common Symptoms
- Red Bumps: Small, red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles are often the first sign of folliculitis.
- Pus-filled Blisters: In more severe cases, these bumps may develop into pus-filled blisters that can be painful or itchy.
- Itching or Burning: Many individuals experience discomfort, including itching or a burning sensation in the affected area.
- Crusting or Scabbing: As the condition progresses, the bumps may crust over or scab, particularly if scratched.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While folliculitis is often mild and can be treated at home, there are times when you should seek medical advice:
- If the symptoms persist for more than a few days despite home treatment.
- If you notice spreading redness or swelling.
- If you develop a fever or feel unwell.
For those dealing with chronic or severe cases, such as folliculitis decalvans, consulting a dermatologist is crucial. They can provide tailored treatment options, which may include medicated shampoos, topical antibiotics, or even oral medications.
In conclusion, understanding folliculitis, its symptoms, and potential treatments can empower you to manage this condition effectively. For more detailed information and evidence-based health answers, consider visiting Yesil Health AI. Remember, early intervention can lead to better outcomes! 🌟

Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed. This inflammation can be caused by various factors, leading to different types of folliculitis. Understanding these types can help in identifying the right treatment and management strategies. Here are the most common types of folliculitis:
Bacterial Folliculitis
Bacterial folliculitis is the most prevalent form, often caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. It typically appears as small, red bumps or pus-filled blisters around hair follicles. This type can occur anywhere on the body but is most common on the scalp, face, and buttocks. Factors such as shaving, tight clothing, and excessive sweating can increase the risk of bacterial folliculitis.
Fungal Folliculitis
Fungal folliculitis is caused by an overgrowth of fungi, particularly Malassezia, which is naturally found on the skin. This type often manifests as itchy, red bumps and is more common in individuals with oily skin or those who use heavy skin products. It can also occur in warm, humid environments, making it a concern for athletes and those who sweat frequently.
Viral Folliculitis
Viral folliculitis is less common and is usually associated with viral infections, such as herpes simplex. This type can cause painful blisters and is often accompanied by other symptoms of viral infection. If you suspect viral folliculitis, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment.
Non-Infectious Folliculitis
This type of folliculitis is not caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses. Instead, it can result from irritation, friction, or allergic reactions to products like shaving creams or hair dyes. Non-infectious folliculitis may appear similar to other types but typically resolves once the irritant is removed.
Folliculitis Decalvans
Folliculitis decalvans is a more severe form that can lead to permanent hair loss. It is characterized by painful, inflamed areas on the scalp and can result in scarring. This type often requires specialized treatment from a dermatologist, as it can be resistant to standard therapies.
Causes of Folliculitis
Understanding the causes of folliculitis is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Several factors can contribute to the development of this condition:
Infections
As mentioned earlier, folliculitis can be caused by bacterial, fungal, or viral infections. Bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus are the most common culprits, while fungi such as Malassezia can also lead to inflammation. Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding sharing personal items can help reduce the risk of infections.
Mechanical Irritation
Mechanical irritation from shaving, tight clothing, or friction can damage hair follicles, making them more susceptible to inflammation. For instance, shaving can create tiny cuts that allow bacteria to enter the skin. To minimize irritation, consider using a sharp razor, shaving in the direction of hair growth, and applying soothing aftershave products.
Excessive Sweating
Excessive sweating can create a warm, moist environment that promotes the growth of bacteria and fungi. This is particularly common in athletes or individuals who work in hot environments. Wearing breathable fabrics and showering promptly after sweating can help prevent folliculitis.
Skin Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions, such as acne or eczema, may be more prone to developing folliculitis. These conditions can compromise the skin barrier, making it easier for pathogens to invade. Proper management of underlying skin issues is essential for preventing folliculitis.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can also play a role in the development of folliculitis. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can lead to increased oil production and clogged pores, creating an environment conducive to folliculitis. If you suspect hormonal issues, consulting a healthcare provider can provide insights into managing symptoms.
In summary, folliculitis can arise from various causes, including infections, mechanical irritation, excessive sweating, skin conditions, and hormonal changes. By understanding these factors, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this common skin condition effectively. 🌟
Risk Factors for Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles, often resulting in red, itchy bumps. Understanding the risk factors associated with folliculitis can help you take preventive measures and seek timely treatment. Here are some key factors that may increase your likelihood of developing this condition:
1. Poor Hygiene
Maintaining proper hygiene is crucial in preventing folliculitis. When sweat, dirt, and bacteria accumulate on the skin, they can clog hair follicles, leading to inflammation. Regularly cleansing your skin, especially after sweating or exercising, can significantly reduce your risk.
2. Shaving and Hair Removal
Shaving can irritate the skin and damage hair follicles, making them more susceptible to infection. This is particularly true for areas like the beard (known as folliculitis barbae) and the scalp. Using a clean, sharp razor and shaving in the direction of hair growth can help minimize irritation.
3. Tight Clothing
Wearing tight clothing can trap moisture and heat against the skin, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth. This is especially relevant for areas prone to friction, such as the buttocks and thighs. Opting for loose-fitting clothing made from breathable fabrics can help reduce this risk.
4. Hot and Humid Environments
Folliculitis is more prevalent in hot and humid conditions, where sweat and moisture can lead to bacterial overgrowth. If you live in such climates, it’s essential to keep your skin dry and clean to prevent outbreaks.
5. Compromised Immune System
Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to chronic illnesses, medications, or other factors, are at a higher risk for developing folliculitis. If you have a condition that affects your immune response, it’s crucial to be vigilant about skin care and hygiene.
6. Certain Medical Conditions
Conditions like diabetes and obesity can increase the risk of folliculitis. These conditions can affect blood circulation and skin health, making it easier for infections to occur. Managing these underlying health issues can help reduce your risk.
7. Use of Antibiotics
While antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial infections, their overuse can lead to antibiotic resistance and disrupt the natural balance of bacteria on the skin. This imbalance can increase the likelihood of developing folliculitis. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or stopping any medication.
Diagnosing Folliculitis
Diagnosing folliculitis typically involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. Understanding the diagnostic process can help you feel more prepared if you suspect you have this condition. Here’s what to expect:
1. Medical History Review
Your doctor will begin by taking a detailed medical history. This includes asking about your symptoms, duration, and any previous skin conditions. Be prepared to discuss your hygiene practices, shaving habits, and any recent changes in your lifestyle or medications.
2. Physical Examination
A physical examination of the affected area is crucial for diagnosis. Your doctor will look for characteristic signs of folliculitis, such as:
- Red, inflamed bumps around hair follicles
- Pus-filled blisters
- Itching or tenderness in the affected area
3. Laboratory Tests
In some cases, your doctor may recommend laboratory tests to determine the underlying cause of folliculitis. This could include:
- Culture tests: A sample from the affected area may be taken to identify the specific bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, a small sample of skin may be taken for further analysis, especially if the diagnosis is unclear.
4. Differential Diagnosis
Folliculitis can resemble other skin conditions, such as acne or eczema. Your doctor will consider these possibilities and may conduct additional tests to rule them out. This step is essential to ensure you receive the most effective treatment.
5. Treatment Recommendations
Once diagnosed, your healthcare provider will discuss treatment options tailored to your specific case. This may include topical or oral antibiotics, antifungal medications, or lifestyle changes to prevent recurrence.
Understanding the risk factors and diagnostic process for folliculitis can empower you to take control of your skin health. If you suspect you have folliculitis, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support. 🌟

Folliculitis Treatment Options
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become inflamed, often due to infection, irritation, or blockage. While it can be uncomfortable and unsightly, there are several effective treatment options available to help manage and alleviate the symptoms. Here, we’ll explore various folliculitis treatment options that can help you regain healthy skin.
Topical Treatments
For mild cases of folliculitis, topical treatments can be quite effective. These include:
- Antibiotic Creams: Over-the-counter or prescription antibiotic creams can help combat bacterial infections. Common options include mupirocin and clindamycin.
- Antifungal Creams: If your folliculitis is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal creams like clotrimazole or ketoconazole may be recommended.
- Medicated Shampoos: For folliculitis on the scalp, using medicated shampoos containing ingredients like salicylic acid or zinc pyrithione can help reduce inflammation and clear up the condition.
Oral Medications
In more severe cases or when topical treatments are ineffective, oral medications may be necessary:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics such as doxycycline or minocycline can be prescribed for bacterial folliculitis, especially if it is recurrent.
- Antifungal Medications: For persistent fungal folliculitis, oral antifungal medications like fluconazole may be recommended.
- Corticosteroids: In cases of inflammation, corticosteroids can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
Home Remedies
Many people find relief from folliculitis symptoms through simple home remedies. Here are a few you might consider:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm compress to the affected area can help soothe irritation and promote healing.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial and antifungal properties, diluted tea tree oil can be applied to the skin to help reduce inflammation.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: This natural remedy can help balance the skin’s pH and has antimicrobial properties. Mix it with water and apply it to the affected area.
When to See a Doctor
If your folliculitis does not improve with home treatments or over-the-counter options, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend a tailored treatment plan. Additionally, if you experience severe pain, fever, or spreading redness, seek medical attention promptly.
Preventing Folliculitis
While treating folliculitis is essential, preventing it from occurring in the first place is equally important. Here are some effective strategies to help you avoid this pesky condition:
Maintain Good Hygiene
Keeping your skin clean is crucial in preventing folliculitis. Here are some tips:
- Shower Regularly: Showering daily, especially after sweating or exercising, can help remove bacteria and prevent clogged follicles.
- Use Gentle Cleansers: Opt for mild, non-irritating soaps and body washes to avoid stripping your skin of its natural oils.
Avoid Tight Clothing
Wearing tight clothing can cause friction and irritation, leading to folliculitis. Choose loose-fitting clothes, especially in hot and humid weather, to allow your skin to breathe.
Shaving Techniques
If you shave regularly, consider the following tips to minimize the risk of folliculitis:
- Use a Clean Razor: Always use a clean, sharp razor to reduce the risk of infection.
- Shave in the Direction of Hair Growth: This can help prevent ingrown hairs and irritation.
- Moisturize After Shaving: Applying a soothing lotion or aftershave can help calm the skin.
Limit Hot Tub and Pool Use
Hot tubs and poorly maintained swimming pools can harbor bacteria that contribute to folliculitis. If you enjoy these activities, ensure that the water is properly treated and avoid using them if you have open wounds or cuts.
Consult a Dermatologist
If you have a history of recurrent folliculitis, consider consulting a dermatologist. They can provide personalized advice and may recommend preventive treatments, such as medicated shampoos or topical solutions, to keep your skin healthy.
By following these preventive measures and understanding your treatment options, you can effectively manage and reduce the occurrence of folliculitis, leading to healthier skin and greater confidence! 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Folliculitis
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, often caused by bacterial or fungal infections. It can appear as red, itchy bumps or pus-filled blisters on the skin.
What are the common causes of Folliculitis?
- Infections (bacterial or fungal)
- Ingrown hairs
- Excessive sweating
- Wearing tight clothing
- Shaving or waxing
How can I treat Folliculitis?
Treatment for folliculitis may include:
- Topical antibiotics or antifungal creams
- Oral antibiotics for severe cases
- Medicated shampoos for scalp folliculitis
- Warm compresses to soothe irritation
What is Folliculitis Decalvans?
Folliculitis decalvans is a chronic form of folliculitis that leads to hair loss and scarring. It primarily affects the scalp and can be more challenging to treat.
Can Folliculitis occur on the scalp?
Yes, folliculitis on the scalp is common and can cause discomfort and hair loss. Treatment may involve medicated shampoos and topical treatments.
Is there a specific shampoo for Folliculitis?
Yes, there are folliculitis shampoos available that contain ingredients like ketoconazole or salicylic acid to help reduce inflammation and combat infections.
How can I prevent Folliculitis?
- Avoid tight clothing that traps moisture
- Practice good hygiene
- Use clean razors and shaving techniques
- Keep skin dry and cool
What should I do if I have Folliculitis on my butt?
If you experience folliculitis on the butt, maintain cleanliness, avoid tight clothing, and consider using topical treatments. If symptoms persist, consult a healthcare professional.
Can Folliculitis be a sign of an underlying condition?
In some cases, folliculitis may indicate an underlying condition, such as an autoimmune disorder. If you have recurrent or severe cases, it’s advisable to seek medical advice.
Are there any home remedies for Folliculitis?
Some home remedies include:
- Applying warm compresses
- Using tea tree oil for its antibacterial properties
- Maintaining a healthy diet to support skin health
When should I see a doctor for Folliculitis?
If you experience persistent symptoms, severe pain, or signs of infection (such as fever or spreading redness), it is important to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment.