What Is Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome (RMS) is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the body’s ability to regulate insulin, leading to severe insulin resistance. This condition is classified as a form of congenital generalized lipodystrophy, which means that individuals with RMS have a significant deficiency of adipose (fat) tissue. The syndrome is named after the two physicians, Dr. Rabson and Dr. Mendenhall, who first described it in the medical literature.
RMS is caused by mutations in the INSR gene, which encodes the insulin receptor. This gene is crucial for the proper functioning of insulin in the body, and when it is mutated, it leads to a range of metabolic issues. Individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome often experience a variety of health challenges, including growth abnormalities, dental issues, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes at a young age.
Understanding the Genetics of RMS
The genetic mutations responsible for Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means that both parents must carry a copy of the mutated gene for their child to be affected by the syndrome. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis, and understanding the genetic basis of RMS is crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Rabson-Mendenhall Symptoms
The symptoms of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can vary widely among individuals, but several common signs and symptoms have been identified. Early diagnosis and management are essential to improve the quality of life for those affected by this syndrome.
Common Symptoms of RMS
- Severe Insulin Resistance: One of the hallmark features of RMS is the body’s inability to respond to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels and an increased risk of diabetes.
- Growth Abnormalities: Children with RMS may experience delayed growth and development, resulting in shorter stature compared to their peers.
- Dental Issues: Many individuals with RMS have dental abnormalities, including missing teeth and malocclusion (misalignment of teeth).
- Skin Changes: Some patients may develop thickened skin or acanthosis nigricans, a condition characterized by dark, velvety patches of skin.
- Hypertrichosis: Increased hair growth in unusual areas can also be a symptom of RMS.
- Fatty Liver Disease: Due to metabolic disturbances, individuals with RMS may be at risk for liver complications, including fatty liver disease.
Long-Term Health Implications
Living with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can pose significant health challenges. The severe insulin resistance often leads to early-onset type 2 diabetes, which can result in complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney problems, and vision issues. Regular monitoring and management of blood sugar levels are crucial for preventing these complications.
Additionally, individuals with RMS may require a multidisciplinary approach to care, involving endocrinologists, nutritionists, and dental specialists to address the various aspects of the syndrome. Early intervention and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and improve overall health outcomes.
Seeking Support and Resources
For those affected by Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome, finding reliable information and support is essential. Resources like Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) provide evidence-based health answers and can help individuals and families navigate the complexities of this rare condition. Connecting with support groups and healthcare professionals who understand RMS can also provide valuable emotional and practical support.
In conclusion, Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome is a complex genetic disorder that requires careful management and support. By understanding the symptoms and implications of RMS, individuals and families can take proactive steps toward better health and well-being. 🌟
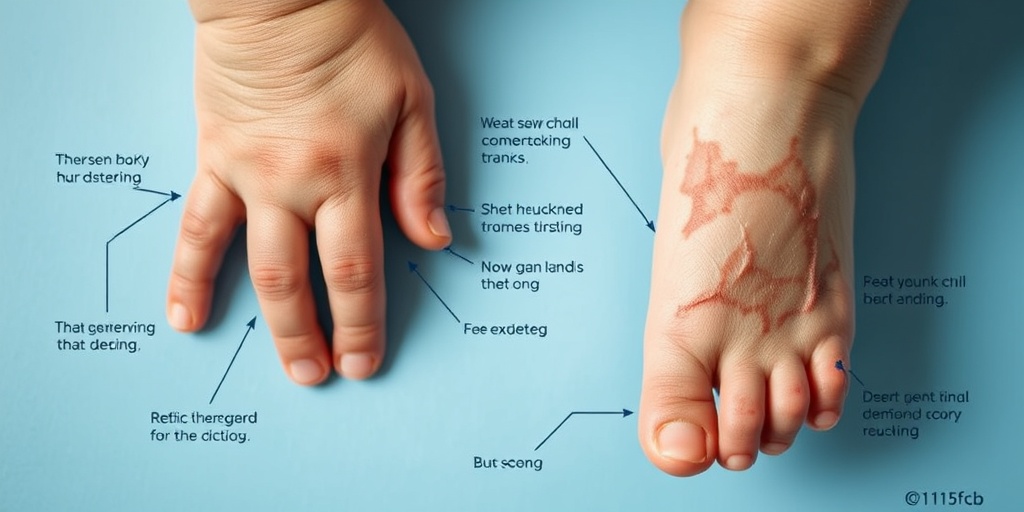
Rabson-Mendenhall Causes
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome (RMS) is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the body’s ability to regulate insulin, leading to severe insulin resistance and various other health complications. Understanding the causes of this syndrome is crucial for effective management and treatment. Let’s delve into the underlying factors that contribute to the development of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome.
Genetic Mutations
The primary cause of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome is genetic mutations. Specifically, mutations in the INSR gene are responsible for this condition. The INSR gene provides instructions for making the insulin receptor, which is essential for the body to respond to insulin. When this gene is mutated, the insulin receptor does not function properly, leading to the characteristic symptoms of RMS.
Inheritance Pattern
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene—one from each parent—to develop the syndrome. Parents who carry one copy of the mutated gene typically do not exhibit symptoms but can pass the mutation to their children. This genetic aspect highlights the importance of family history in understanding the risk of developing RMS.
Associated Conditions
Individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome often experience other health issues, which can complicate the understanding of its causes. Some of these associated conditions include:
- Severe insulin resistance: This is the hallmark of RMS, leading to high blood sugar levels and potential diabetes.
- Hyperandrogenism: Increased levels of androgens can lead to symptoms such as hirsutism and menstrual irregularities in females.
- Growth abnormalities: Many individuals with RMS experience growth delays or abnormalities due to hormonal imbalances.
These associated conditions can sometimes obscure the direct causes of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome, making it essential for healthcare providers to conduct thorough evaluations.
Rabson-Mendenhall Diagnosis
Diagnosing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can be challenging due to its rarity and the overlap of symptoms with other conditions. However, a combination of clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory assessments can lead to an accurate diagnosis. Here’s how healthcare professionals typically approach the diagnosis of RMS.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome is a comprehensive clinical evaluation. Healthcare providers will look for the following key symptoms:
- Severe insulin resistance: This is often indicated by high blood sugar levels that do not respond well to standard diabetes treatments.
- Physical characteristics: Patients may exhibit distinct physical features, including thickened skin, dental abnormalities, and growth delays.
- Hormonal imbalances: Symptoms related to hyperandrogenism, such as excessive hair growth or irregular menstrual cycles, may also be present.
Genetic Testing
Once a healthcare provider suspects Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome, genetic testing is often recommended. This testing can confirm the presence of mutations in the INSR gene. Genetic testing is crucial not only for diagnosis but also for understanding the inheritance pattern and potential implications for family members.
Laboratory Assessments
In addition to genetic testing, laboratory assessments play a vital role in diagnosing RMS. These may include:
- Blood tests: To measure insulin levels, blood sugar levels, and hormone levels.
- Oral glucose tolerance test: This test helps assess how well the body processes glucose.
- Growth hormone tests: To evaluate any growth abnormalities that may be present.
These assessments help healthcare providers understand the extent of insulin resistance and any associated complications, leading to a more comprehensive diagnosis.
In conclusion, diagnosing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome involves a multifaceted approach that combines clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and laboratory assessments. Understanding the causes and diagnostic methods is essential for effective management and treatment of this complex condition. 🩺

Rabson-Mendenhall Treatment Options
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome (RMS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects various bodily functions, particularly those related to insulin regulation and growth. Understanding the treatment options available for this condition is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here, we will explore the primary treatment options for individuals diagnosed with RMS.
Insulin Therapy
One of the most significant challenges faced by individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome is insulin resistance, which can lead to severe diabetes. Insulin therapy is often the cornerstone of treatment. This involves administering insulin to help regulate blood sugar levels effectively. The type and dosage of insulin can vary based on individual needs, and regular monitoring is essential to ensure optimal management.
Growth Hormone Therapy
Many individuals with RMS experience growth deficiencies due to hormonal imbalances. Growth hormone therapy may be recommended to help stimulate growth and development. This treatment can be particularly beneficial during childhood and adolescence, as it can help achieve a more typical height and improve overall physical health.
Dietary Management
Nutrition plays a vital role in managing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome. A well-balanced diet tailored to the individual’s needs can help control blood sugar levels and support overall health. Consulting with a registered dietitian who specializes in metabolic disorders can provide personalized dietary recommendations. Key dietary strategies may include:
- Low Glycemic Index Foods: Incorporating foods that have a low glycemic index can help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Regular Meal Timing: Eating at consistent times can aid in maintaining steady insulin levels.
- Balanced Macronutrients: Ensuring a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential for overall health.
Regular Monitoring and Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups are crucial for individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome. These appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor growth, metabolic function, and any potential complications. Blood tests to check insulin levels, glucose levels, and hormone levels are typically part of this ongoing assessment.
Supportive Therapies
In addition to medical treatments, supportive therapies can play a significant role in managing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome. These may include:
- Physical Therapy: To improve mobility and strength, especially if growth deficiencies affect physical development.
- Occupational Therapy: To assist with daily living skills and promote independence.
- Psychological Support: Counseling or support groups can help individuals and families cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
Rabson-Mendenhall Management Strategies
Managing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome effectively requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing support. Here are some key management strategies that can help individuals with RMS lead healthier lives.
Personalized Care Plans
Each individual with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome may experience different symptoms and challenges. Therefore, personalized care plans are essential. These plans should be developed in collaboration with a healthcare team, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and other specialists. Tailoring the management approach to the individual’s specific needs can significantly enhance treatment outcomes.
Education and Awareness
Education is a powerful tool in managing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome. Understanding the condition, its symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals and their families to make informed decisions. Resources such as support groups, online forums, and educational materials can provide valuable information and foster a sense of community.
Regular Physical Activity
Incorporating regular physical activity into daily routines can have numerous benefits for individuals with RMS. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, supports cardiovascular health, and enhances overall well-being. Activities can range from walking and swimming to more structured exercise programs, depending on the individual’s abilities and preferences.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Living with a chronic condition like Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can be emotionally challenging. Seeking emotional and psychological support is vital for both individuals and their families. This support can come from mental health professionals, support groups, or online communities where experiences and coping strategies can be shared.
Advocacy and Research Participation
Engaging in advocacy efforts and participating in research studies can contribute to a better understanding of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome. By being involved in research, individuals can help advance knowledge about the condition and potentially benefit from new treatment options as they become available.
In conclusion, managing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome involves a multifaceted approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and emotional support. By implementing these strategies, individuals can improve their quality of life and navigate the challenges associated with this rare condition more effectively. 🌟

Rabson-Mendenhall Genetic Factors
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome (RMS) is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the body’s ability to regulate insulin, leading to severe insulin resistance and a host of related health issues. Understanding the genetic factors behind this syndrome is crucial for both diagnosis and management.
The Genetic Basis of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome
RMS is caused by mutations in the INSR gene, which encodes the insulin receptor. This receptor is essential for the body’s ability to respond to insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. When mutations occur in the INSR gene, the insulin receptor becomes dysfunctional, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the syndrome.
Inheritance Patterns
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. This means that an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene—one from each parent—to develop the condition. If both parents are carriers of the mutation, there is a 25% chance with each pregnancy that their child will inherit the syndrome.
Common Genetic Mutations
Several specific mutations in the INSR gene have been identified in individuals with RMS. These mutations can vary widely, leading to different degrees of severity in symptoms. Some of the most common mutations include:
- Missense mutations: These mutations result in a single amino acid change in the insulin receptor, which can significantly affect its function.
- Nonsense mutations: These lead to a premature stop codon in the protein sequence, resulting in a nonfunctional receptor.
- Frameshift mutations: These occur when nucleotides are inserted or deleted, altering the reading frame of the gene and producing a dysfunctional protein.
Genetic Testing and Counseling
For families with a history of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome, genetic testing can provide valuable information. Testing can confirm the presence of mutations in the INSR gene, helping to clarify the diagnosis. Genetic counseling is also recommended for affected families, as it can help them understand the risks of passing the condition to future generations and discuss potential management strategies.
Rabson-Mendenhall Outlook and Prognosis
The outlook for individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can vary significantly based on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of management strategies. Understanding the prognosis is essential for families and healthcare providers to plan appropriate care.
Life Expectancy
While there is limited data on the life expectancy of individuals with RMS, many affected individuals can lead relatively normal lives with proper management. However, complications related to severe insulin resistance, such as diabetes and cardiovascular issues, can impact overall health and longevity. Regular monitoring and proactive management of these complications are crucial.
Management Strategies
Managing Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
- Insulin therapy: Since individuals with RMS have insulin resistance, they may require higher doses of insulin or alternative medications to help control blood sugar levels.
- Dietary modifications: A balanced diet low in simple sugars and high in fiber can help manage blood glucose levels effectively.
- Regular monitoring: Frequent blood sugar monitoring is essential to prevent complications and adjust treatment as needed.
- Supportive therapies: Physical therapy and counseling may be beneficial for addressing any developmental or psychological challenges associated with the syndrome.
Long-Term Outlook
With appropriate treatment and lifestyle adjustments, many individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can achieve a good quality of life. Early intervention and ongoing care are key factors in improving outcomes. Families should work closely with healthcare providers to develop a comprehensive care plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
In conclusion, while Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome presents significant challenges, understanding its genetic factors and prognosis can empower families and individuals to navigate the complexities of this rare condition effectively. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome
What is Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by a combination of symptoms including growth abnormalities, insulin resistance, and distinctive facial features. It is caused by mutations in the INS gene, which plays a crucial role in insulin production.
What are the symptoms of Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
Individuals with this syndrome may experience a variety of symptoms, including:
- Growth retardation
- Insulin resistance
- Distinctive facial features such as a broad forehead and thick lips
- Dental abnormalities
- Skin changes including thickened skin
What is the life expectancy for someone with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
The life expectancy for individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can vary significantly based on the severity of symptoms and associated complications. Early diagnosis and management of symptoms can improve quality of life and potentially extend life expectancy.
How is Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome treated?
Treatment for Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome typically focuses on managing symptoms and may include:
- Insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels
- Growth hormone therapy for growth-related issues
- Regular monitoring of metabolic health
Consultation with a healthcare provider specializing in genetic disorders is essential for personalized treatment plans.
What causes Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
This syndrome is primarily caused by mutations in the INS gene, which affects insulin production and leads to the various symptoms associated with the condition. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, meaning both parents must carry the mutated gene for a child to be affected.
Where can I find more information about Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
For more detailed information, you can refer to resources such as:
Is there a specific ICD-10 code for Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
Yes, Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome has a specific ICD-10 code, which is E13.8. This code is used for billing and documentation purposes in healthcare settings.
Can Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome lead to diabetes?
Yes, individuals with Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome often experience insulin resistance, which can lead to diabetes. Proper management of insulin levels and regular monitoring are crucial to prevent complications associated with diabetes.
Are there any support groups for Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome?
Yes, there are support groups and online communities where individuals and families affected by Rabson-Mendenhall Syndrome can connect, share experiences, and access resources. These groups can provide valuable emotional support and information.




