What Is Scarring Bullosa?
Scarring Bullosa is a rare and complex skin condition that falls under the umbrella of epidermolysis bullosa (EB). This genetic disorder is characterized by extreme fragility of the skin, leading to blister formation with minimal friction or trauma. Individuals with this condition often experience painful blisters that can result in significant scarring over time. The term “bullosa” refers to the blisters that form, while “scarring” highlights the long-term effects these blisters can have on the skin.
The Genetics Behind Scarring Bullosa
Scarring Bullosa is primarily caused by mutations in genes responsible for producing proteins that help anchor the layers of the skin together. These mutations lead to a deficiency in structural proteins, making the skin more susceptible to damage. The most common types of EB associated with scarring include:
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB): This type is characterized by scarring and can lead to severe complications, including fusion of fingers and toes.
- Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa (JEB): While less common, JEB can also result in scarring and is often more severe in its presentation.
Understanding the genetic basis of Scarring Bullosa is crucial for developing targeted therapies and improving patient outcomes. Genetic counseling can provide families with valuable information about the inheritance patterns and risks associated with this condition.
How Scarring Bullosa Affects Daily Life
Living with Scarring Bullosa can be challenging. The constant risk of blistering can lead to anxiety and a need for careful management of daily activities. Individuals may need to take extra precautions, such as wearing protective clothing and avoiding activities that could cause skin trauma. This condition can also impact social interactions and mental health, as visible scars and the need for ongoing care can lead to feelings of isolation.
Scarring Bullosa Symptoms
The symptoms of Scarring Bullosa can vary significantly from person to person, depending on the severity of the condition and the specific type of EB. However, some common symptoms include:
1. Blister Formation
The hallmark of Scarring Bullosa is the formation of blisters, which can occur on any part of the body, including the hands, feet, and mucous membranes. These blisters can be:
- Painful: Blisters can cause significant discomfort, especially if they rupture.
- Recurrent: New blisters may form frequently, leading to a cycle of healing and new injury.
2. Scarring
As blisters heal, they often leave behind scars that can be thick, discolored, and sometimes contractile, leading to restricted movement in affected areas. Over time, these scars can accumulate, resulting in:
- Skin Tightness: Scarring can cause the skin to become tight, limiting mobility.
- Deformities: In severe cases, scarring can lead to deformities in fingers and toes.
3. Increased Risk of Infections
Open blisters can serve as entry points for bacteria, increasing the risk of skin infections. Individuals with Scarring Bullosa must be vigilant about wound care and may require antibiotics to manage infections.
4. Pain and Discomfort
Chronic pain is a common complaint among individuals with Scarring Bullosa. This pain can stem from blister formation, scarring, and the overall fragility of the skin. Effective pain management strategies are essential for improving quality of life.
5. Psychological Impact
The visible nature of Scarring Bullosa can lead to psychological challenges, including anxiety and depression. Support from mental health professionals and support groups can be invaluable for individuals coping with the emotional aspects of this condition.
For those seeking more information about Scarring Bullosa and its management, resources like Yesil Health AI (yesilhealth.com) can provide evidence-based answers and support. Understanding the condition is the first step toward effective management and improving quality of life.
In conclusion, Scarring Bullosa is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to care. By recognizing the symptoms and understanding the underlying causes, individuals and their families can better navigate the challenges associated with this condition. 🌼
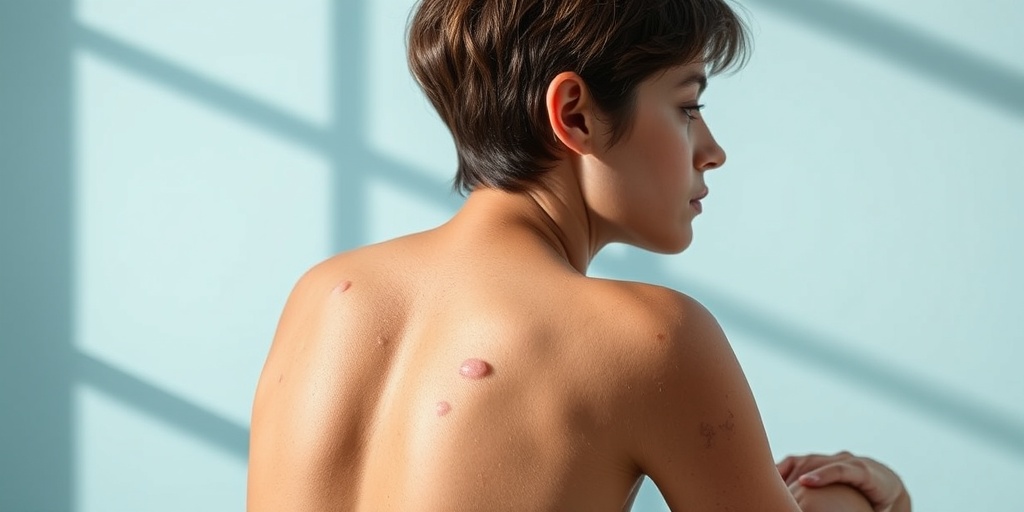
Causes of Scarring Bullosa
Scarring Bullosa, often associated with a group of genetic disorders known as Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB), is primarily characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily. Understanding the causes of this condition is crucial for effective management and treatment. Let’s delve into the underlying factors that contribute to Scarring Bullosa.
Genetic Mutations
The primary cause of Scarring Bullosa is genetic mutations that affect the proteins responsible for skin integrity. These mutations can occur in various genes, including:
- COL7A1: This gene is crucial for producing type VII collagen, which helps anchor the epidermis to the dermis. Mutations here can lead to severe forms of EB.
- KRT14 and KRT5: These keratin genes are essential for the structural integrity of the skin. Mutations can result in increased fragility and blistering.
- LAMB3: This gene is involved in the formation of the basement membrane, and its mutations can lead to junctional EB, a type of Scarring Bullosa.
These genetic defects can be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, meaning that a child can inherit the condition from one or both parents. In some cases, the mutations can occur spontaneously, leading to new cases of Scarring Bullosa without a family history.
Environmental Factors
While genetic factors play a significant role, environmental influences can also exacerbate the condition. Factors such as:
- Friction and Trauma: Everyday activities that cause friction on the skin can lead to blister formation. This is particularly problematic for individuals with Scarring Bullosa, as their skin is already compromised.
- Infections: Skin infections can worsen the condition, leading to increased blistering and scarring.
- Sun Exposure: Ultraviolet (UV) radiation can damage fragile skin, making it more susceptible to blistering and scarring.
Understanding these causes can help individuals and caregivers take preventive measures to protect the skin and minimize the risk of blistering.
Risk Factors for Scarring Bullosa
Identifying the risk factors associated with Scarring Bullosa is essential for early diagnosis and intervention. While the condition is primarily genetic, several factors can increase the likelihood of developing this skin disorder.
Family History
One of the most significant risk factors for Scarring Bullosa is a family history of Epidermolysis Bullosa. If a parent carries a mutation associated with EB, there is a higher chance that their children may inherit the condition. Genetic counseling can be beneficial for families with a history of EB to understand their risks and options.
Type of Epidermolysis Bullosa
There are several types of Epidermolysis Bullosa, each with varying degrees of severity and risk factors:
- Simplex EB: This is the most common form and is often less severe, but individuals can still experience blistering.
- Dystrophic EB: This type is associated with more severe scarring and can lead to significant complications.
- Junctional EB: This rare form can be life-threatening and is characterized by severe blistering and scarring.
Understanding the specific type of EB can help in assessing the risk and planning appropriate care.
Age and Gender
While Scarring Bullosa can affect individuals of any age, it is often diagnosed in infancy or early childhood. Additionally, some studies suggest that males may be more frequently affected than females, although the reasons for this disparity are not entirely understood.
Other Health Conditions
Individuals with other health conditions that compromise skin integrity or immune function may also be at increased risk for developing Scarring Bullosa. Conditions such as:
- Autoimmune Disorders: These can lead to skin fragility and increase the likelihood of blistering.
- Genetic Syndromes: Certain syndromes that affect connective tissue can also predispose individuals to skin issues.
Recognizing these risk factors can empower individuals and families to seek early intervention and support, ultimately improving quality of life for those affected by Scarring Bullosa. 🌟
Diagnosing Scarring Bullosa
Diagnosing Scarring Bullosa, a severe form of epidermolysis bullosa (EB), can be a complex process. This condition is characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily, leading to significant scarring over time. Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective management and treatment.
Clinical Evaluation
The first step in diagnosing Scarring Bullosa typically involves a thorough clinical evaluation. A healthcare provider will assess the patient’s medical history and conduct a physical examination. Key indicators include:
- Skin Blistering: Frequent and severe blistering, especially in response to minor trauma.
- Scarring: The presence of scars from previous blisters, which can be a hallmark of the condition.
- Family History: A history of EB or related skin conditions in the family may suggest a genetic predisposition.
Genetic Testing
To confirm a diagnosis of Scarring Bullosa, genetic testing is often recommended. This testing can identify mutations in the genes responsible for the condition, such as the COL7A1 gene, which is commonly associated with dystrophic EB. Genetic testing not only aids in diagnosis but also helps in understanding the specific type of EB, which can influence treatment options.
Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy may also be performed to examine the structure of the skin at a microscopic level. This procedure involves taking a small sample of skin and analyzing it for:
- Blister Formation: Observing where the blister forms can help differentiate between types of EB.
- Collagen Analysis: Evaluating collagen production and structure, which can be affected in Scarring Bullosa.
Immunofluorescence Studies
Immunofluorescence studies can further assist in diagnosing Scarring Bullosa. This technique uses antibodies to detect specific proteins in the skin, providing insight into the underlying causes of blistering and scarring.
Complications of Scarring Bullosa
While Scarring Bullosa primarily affects the skin, it can lead to a range of complications that impact overall health and quality of life. Understanding these complications is essential for effective management.
Infection Risk
One of the most significant complications associated with Scarring Bullosa is the increased risk of skin infections. The frequent blistering and open wounds create an entry point for bacteria, leading to:
- Cellulitis: A common bacterial skin infection that can cause redness, swelling, and pain.
- Sepsis: In severe cases, infections can enter the bloodstream, leading to life-threatening conditions.
Chronic Pain and Discomfort
Individuals with Scarring Bullosa often experience chronic pain due to repeated blistering and scarring. This pain can significantly affect daily activities and overall quality of life. Effective pain management strategies are crucial and may include:
- Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments to soothe the skin.
- Oral Medications: Pain relievers or anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Physical Therapy: To maintain mobility and reduce discomfort.
Scarring and Contractures
As the name suggests, Scarring Bullosa leads to significant scarring, which can result in contractures—tightening of the skin that restricts movement. This can affect:
- Joint Mobility: Limiting the range of motion in affected areas.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Visible scars can impact self-esteem and body image.
Psychosocial Impact
The physical challenges of living with Scarring Bullosa can also lead to psychosocial issues. Individuals may experience:
- Anxiety and Depression: Due to chronic pain and visible scars.
- Social Isolation: Fear of stigma or misunderstanding from others can lead to withdrawal.
Addressing these psychosocial aspects is vital for holistic care, often requiring support from mental health professionals and support groups.
In conclusion, diagnosing and managing Scarring Bullosa involves a comprehensive approach that addresses both the physical and emotional challenges associated with this condition. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and enhance the quality of life for those affected. 🌼

Treatment Options for Scarring Bullosa
Scarring Bullosa, often associated with epidermolysis bullosa (EB), is a rare genetic condition characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily. Managing this condition requires a comprehensive approach tailored to the individual’s needs. Here, we explore various treatment options available for those living with Scarring Bullosa.
Wound Care Management
One of the most critical aspects of treating Scarring Bullosa is effective wound care. Proper management can significantly reduce the risk of infection and promote healing. Here are some essential tips:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use mild, non-irritating cleansers to clean blisters and wounds.
- Moisturizing: Keeping the skin hydrated can help prevent further blistering. Look for emollient creams that are free from fragrances and harsh chemicals.
- Dressings: Specialized dressings can protect blisters and wounds. Hydrocolloid or silicone dressings are often recommended for their gentle adherence and moisture-retentive properties.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms associated with Scarring Bullosa:
- Topical Antibiotics: These can help prevent infections in open wounds.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications may be necessary to manage discomfort.
- Systemic Treatments: In severe cases, systemic treatments such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants may be considered to reduce inflammation and blister formation.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in maintaining mobility and function for individuals with Scarring Bullosa. Regular sessions can help:
- Improve Flexibility: Stretching exercises can prevent contractures and maintain joint mobility.
- Enhance Strength: Strength training can support overall physical health and improve quality of life.
- Promote Skin Health: Therapists can provide guidance on safe exercises that minimize skin trauma.
Psychosocial Support
Living with a chronic condition like Scarring Bullosa can take a toll on mental health. Seeking psychosocial support is crucial:
- Counseling: Professional counseling can help individuals cope with the emotional challenges of living with a visible condition.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide comfort and understanding.
- Education: Learning about the condition can empower patients and families to make informed decisions about care.
Living with Scarring Bullosa
Living with Scarring Bullosa presents unique challenges, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some insights into navigating daily life with this condition.
Daily Skin Care Routine
Establishing a daily skin care routine is essential for managing Scarring Bullosa. Here are some tips to consider:
- Regular Inspections: Check the skin daily for any new blisters or signs of infection.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated from the inside out.
- Sun Protection: Use sunscreen to protect sensitive skin from UV damage, which can exacerbate blistering.
Adapting Lifestyle Choices
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve quality of life:
- Clothing Choices: Opt for loose-fitting, breathable fabrics to minimize friction and irritation.
- Activity Modifications: Engage in low-impact activities that reduce the risk of skin trauma, such as swimming or yoga.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can support skin health and overall well-being.
Building a Support Network
Having a strong support network is invaluable for individuals with Scarring Bullosa. Here are ways to build and maintain connections:
- Family Involvement: Educate family members about the condition to foster understanding and support.
- Community Resources: Utilize local and online resources to connect with others facing similar challenges.
- Advocacy: Get involved in advocacy groups to raise awareness and promote research for Scarring Bullosa.
Living with Scarring Bullosa may require adjustments and ongoing care, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can thrive and lead fulfilling lives. 🌟

Frequently Asked Questions about Scarring Bullosa
What is Scarring Bullosa?
Scarring Bullosa refers to a group of genetic skin disorders characterized by fragile skin that blisters easily. These blisters can lead to scarring and significant skin damage over time. The most common form is epidermolysis bullosa (EB), which is caused by defects in the proteins that help anchor the skin layers together.
What causes Scarring Bullosa?
The primary cause of Scarring Bullosa is genetic mutations that affect the skin’s structural proteins. These mutations can lead to various forms of EB, each with different severity levels and symptoms. The condition is inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, depending on the specific type of EB.
What are the symptoms of Scarring Bullosa?
- Frequent skin blistering
- Severe pain and discomfort
- Scarring and skin thickening
- Increased risk of infections
- Potential complications affecting other organs
How is Scarring Bullosa diagnosed?
Diagnosis of Scarring Bullosa typically involves a combination of physical examinations, family history assessments, and genetic testing. A dermatologist may perform a skin biopsy to analyze the skin structure and identify the specific type of EB.
What treatments are available for Scarring Bullosa?
While there is currently no cure for Scarring Bullosa, treatments focus on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Common approaches include:
- Wound care and dressing changes
- Pain management
- Antibiotics for infections
- Physical therapy to maintain mobility
- Supportive care and counseling
Can Scarring Bullosa lead to other health issues?
Yes, individuals with Scarring Bullosa may face various health challenges, including:
- Increased risk of skin cancer due to chronic skin damage
- Dental issues from oral blistering
- Growth and developmental delays in children
- Emotional and psychological impacts due to the visible nature of the condition
Is there support available for those with Scarring Bullosa?
Absolutely! There are numerous support groups and organizations dedicated to helping individuals and families affected by Scarring Bullosa. These resources provide valuable information, emotional support, and community connections. 🌟
What should I do if I suspect I have Scarring Bullosa?
If you suspect you or a loved one may have Scarring Bullosa, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional or a dermatologist. Early diagnosis and management can significantly improve quality of life and reduce complications.




