What Is Skin Cancer Screening?
Skin cancer screening is a crucial process aimed at detecting skin cancer in its early stages, when it is most treatable. This screening typically involves a thorough examination of the skin by a healthcare professional, who looks for any unusual moles, growths, or changes in the skin’s appearance. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes and survival rates, making regular screenings an essential part of proactive health care.
Why Is Skin Cancer Screening Important?
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and its incidence has been rising steadily over the years. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, one in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. Regular skin cancer screenings can help identify potential issues before they develop into more serious conditions. Here are some key reasons why skin cancer screening is important:
- Early Detection: Finding skin cancer early increases the chances of successful treatment.
- Prevention: Screening can help identify precancerous lesions, allowing for timely intervention.
- Education: Screenings often include education on how to perform self-exams and recognize warning signs.
Who Should Get Screened?
While anyone can develop skin cancer, certain individuals are at a higher risk and should consider regular screenings. These include:
- Individuals with a family history of skin cancer.
- People with fair skin, light hair, and light eyes.
- Those who have had excessive sun exposure or sunburns.
- Individuals with a history of tanning bed use.
Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the appropriate screening schedule based on personal risk factors.
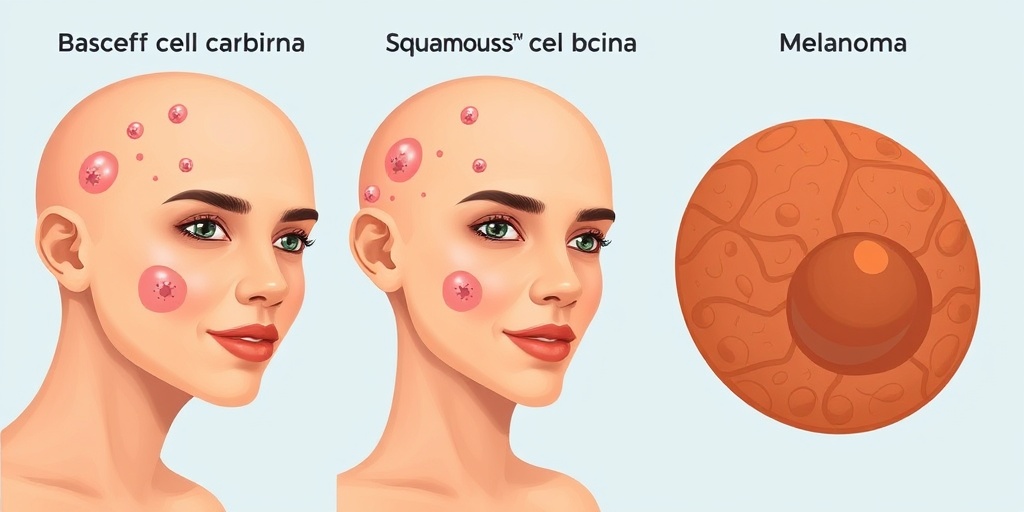
Types of Skin Cancer
Understanding the different types of skin cancer is essential for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. The three most common types of skin cancer are:
1. Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell carcinoma is the most prevalent form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80% of all cases. It typically appears as a small, shiny bump or a pinkish patch on sun-exposed areas of the skin, such as the face, neck, and ears. BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, but it can cause significant local damage if left untreated.
2. Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a firm, red nodule or a flat sore that crusts or bleeds. SCC can develop on sun-exposed areas, but it can also occur in scars or chronic skin sores. While SCC is more aggressive than BCC, it is still highly treatable when detected early.
3. Melanoma
Melanoma is the most serious type of skin cancer, known for its ability to spread rapidly to other parts of the body. It typically appears as a dark mole or a change in an existing mole’s appearance. The ABCDE rule can help identify potential melanomas:
- A: Asymmetry – one half of the mole doesn’t match the other.
- B: Border – irregular or scalloped edges.
- C: Color – varied colors, including shades of brown, black, or even red.
- D: Diameter – larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- E: Evolving – any change in size, shape, or color.
Melanoma requires prompt treatment, as it can be life-threatening if not addressed early.
Conclusion
Skin cancer screening is a vital tool in the fight against skin cancer. By understanding the types of skin cancer and recognizing the importance of regular screenings, individuals can take proactive steps toward their health. If you’re considering a skin cancer screening, resources like Yesil Health AI can provide evidence-based answers to your questions and guide you through the process. Remember, early detection is key to successful treatment! 🌞
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Understanding the risk factors for skin cancer is crucial for prevention and early detection. Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and knowing what increases your risk can help you take proactive measures. Here are some of the primary risk factors to consider:
1. UV Radiation Exposure
One of the leading causes of skin cancer is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. This can come from:
- Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to the sun, especially during peak hours, increases your risk.
- Tanning Beds: Artificial sources of UV light can be just as harmful as natural sunlight.
2. Skin Type
Your skin type plays a significant role in your susceptibility to skin cancer. Individuals with the following characteristics are at a higher risk:
- Fair Skin: People with light skin, freckles, or red or blonde hair are more vulnerable.
- Light Eyes: Those with blue or green eyes have less melanin, which offers less protection against UV rays.
3. Family History
If you have a family history of skin cancer, your risk increases significantly. Genetics can play a role in how your body responds to UV exposure and how effectively it can repair skin damage.
4. Age
As we age, our skin undergoes changes that can increase the risk of skin cancer. Older adults are generally at a higher risk due to cumulative sun exposure over the years.
5. Weakened Immune System
Individuals with compromised immune systems, whether due to medical conditions or medications, are at a greater risk for developing skin cancer. This includes:
- People undergoing chemotherapy
- Those with autoimmune diseases
6. Previous Skin Cancer Diagnosis
If you have had skin cancer in the past, your chances of developing it again are significantly higher. Regular skin cancer screenings are essential for early detection and management.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Being aware of the signs and symptoms of skin cancer can lead to early detection, which is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some key indicators to look out for:
1. Changes in Moles
Monitor any existing moles for changes in size, shape, or color. The ABCDE rule can help you remember what to look for:
- A: Asymmetry – One half of the mole doesn’t match the other.
- B: Border – Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges.
- C: Color – Varied colors (brown, black, tan, red, white, or blue).
- D: Diameter – Larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- E: Evolving – Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
2. New Growths
Keep an eye out for any new growths on your skin, especially if they appear suddenly. These can be flat or raised and may vary in color.
3. Itching or Pain
Any persistent itching, tenderness, or pain in a particular area of your skin should not be ignored. These sensations can indicate underlying issues that require medical attention.
4. Non-Healing Sores
Sores that do not heal or that bleed easily can be a sign of skin cancer. If you notice a sore that persists for more than a few weeks, consult a healthcare professional.
5. Scaly Patches
Rough, scaly patches on the skin, particularly in sun-exposed areas, can be precursors to skin cancer. These patches may be red, brown, or skin-colored and should be evaluated by a doctor.
Regular skin cancer screenings are essential for early detection and can significantly improve outcomes. If you notice any of these signs or have concerns about your skin, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Remember, early intervention is key! 🌞

Screening Methods Explained
When it comes to skin cancer screening, understanding the various methods available can empower you to take charge of your skin health. Early detection is crucial, as it significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. Here, we’ll explore the most common screening methods used to identify skin cancer.
Visual Skin Examination
The most straightforward method of screening is a visual skin examination. This is typically performed by a dermatologist or healthcare provider. During this examination, the doctor will:
- Inspect your skin for any unusual moles or growths.
- Look for changes in existing moles, such as size, shape, or color.
- Assess any areas of concern that may require further investigation.
It’s recommended that adults have a visual skin examination at least once a year, especially if they have a history of skin cancer or other risk factors.
Self-Examination
In addition to professional screenings, performing regular self-examinations is essential. Here’s how you can do it:
- Use a full-length mirror and a hand-held mirror to check all areas of your skin.
- Look for any new moles or changes in existing moles.
- Pay attention to areas that are often overlooked, such as your scalp, between your toes, and under your nails.
Self-examinations should be done monthly, and if you notice any changes, consult your healthcare provider promptly. 🕵️♂️
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy is a specialized technique that allows dermatologists to examine moles and skin lesions more closely. Using a dermatoscope, a handheld device with a magnifying lens and light, doctors can see structures in the skin that are not visible to the naked eye. This method helps in distinguishing between benign and malignant lesions, reducing unnecessary biopsies.
Skin Biopsy
If a suspicious mole or lesion is identified during a visual examination or dermatoscopy, a skin biopsy may be performed. This involves removing a small sample of skin tissue for laboratory analysis. There are several types of biopsies:
- Shave biopsy: A thin layer of skin is shaved off.
- Excisional biopsy: The entire mole or lesion is removed.
- Punch biopsy: A circular tool is used to remove a deeper section of skin.
Biopsies are crucial for confirming a diagnosis of skin cancer and determining the appropriate treatment plan. 🩺
Imaging Tests
In some cases, imaging tests such as CT scans or MRIs may be used to check for skin cancer that has spread beyond the skin. These tests are not typically part of routine screening but may be necessary if skin cancer is diagnosed.
Who Should Get Screened?
Understanding who should undergo skin cancer screening is vital for early detection and prevention. Certain factors increase the risk of developing skin cancer, making regular screenings essential for those individuals.
High-Risk Individuals
People with the following characteristics should prioritize skin cancer screenings:
- Fair skin: Individuals with light skin, freckles, or red or blonde hair are at a higher risk.
- Family history: A family history of skin cancer increases your risk.
- Previous skin cancer: If you’ve had skin cancer before, regular screenings are crucial.
- Excessive sun exposure: Those who have spent significant time in the sun or use tanning beds should be vigilant.
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with conditions that weaken the immune system or those on immunosuppressive medications should get screened regularly.
Age Considerations
While skin cancer can affect individuals of any age, the risk increases as you get older. Adults over the age of 50 should consider annual screenings, especially if they have any risk factors mentioned above. However, younger individuals with risk factors should also be proactive about their skin health.
Regular Check-Ups
Even if you don’t fall into a high-risk category, it’s still wise to have regular skin checks. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that everyone perform self-examinations and consult a dermatologist for a professional evaluation at least once a year. Early detection can save lives! 🌟
In conclusion, understanding the various screening methods and knowing who should get screened can significantly impact skin cancer outcomes. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your skin health!

Benefits of Early Detection
When it comes to skin cancer screening, early detection can be a game-changer. Understanding the benefits of catching skin cancer in its initial stages can empower you to take proactive steps for your health. Here are some key advantages:
Improved Survival Rates
One of the most significant benefits of early detection is the increased survival rate. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, when skin cancer is detected early, the five-year survival rate for melanoma is around 99%. This starkly contrasts with late-stage diagnoses, where survival rates drop significantly. Early detection allows for timely intervention, which can be life-saving.
Less Aggressive Treatment
Early-stage skin cancers often require less aggressive treatment options. For instance, localized skin cancers may be treated with simple surgical excision or topical therapies, which are less invasive than chemotherapy or radiation required for advanced stages. This means fewer side effects and a quicker recovery time for patients.
Cost-Effectiveness
While the cost of skin cancer screening can vary, early detection can ultimately save you money. Treating advanced skin cancer can lead to extensive medical bills due to hospital stays, surgeries, and ongoing treatments. By investing in regular screenings, you may avoid these high costs associated with late-stage cancer treatment.
Peace of Mind
Regular screenings can provide peace of mind. Knowing that you are taking proactive steps to monitor your skin health can alleviate anxiety about potential skin cancer. If any suspicious lesions are found, you can address them promptly, reducing the stress of uncertainty.
Education and Awareness
Participating in skin cancer screenings often comes with educational resources. During your visit, healthcare professionals can provide valuable information about skin health, sun protection, and self-examination techniques. This knowledge empowers you to take charge of your skin health and recognize changes that may require further evaluation.
What to Expect During a Screening
Understanding what to expect during a skin cancer screening can help ease any apprehensions you may have. Here’s a breakdown of the typical process:
Initial Consultation
Your screening will usually begin with a consultation where the dermatologist will ask about your medical history, family history of skin cancer, and any concerns you may have regarding your skin. This is a great time to discuss any moles or spots that have changed in appearance.
Physical Examination
Next, the dermatologist will conduct a thorough physical examination of your skin. This includes:
- Inspecting your entire body, including areas that are often overlooked, such as your scalp, between your toes, and under your nails.
- Using a dermatoscope, a specialized tool that allows for a closer look at moles and skin lesions.
This examination typically lasts about 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the number of moles and the complexity of your skin type.
Biopsy (if necessary)
If the dermatologist identifies any suspicious areas, they may recommend a biopsy. This involves removing a small sample of skin tissue for laboratory analysis. There are different types of biopsies, including:
- Shave biopsy: A small section of the skin is shaved off.
- Excisional biopsy: The entire mole or lesion is removed.
- Punch biopsy: A circular tool is used to remove a deeper layer of skin.
Biopsies are usually quick procedures and can be done in the dermatologist’s office with minimal discomfort.
Follow-Up
After your screening, the dermatologist will discuss the findings with you. If a biopsy was performed, you will receive results within a week or two. Depending on the results, further treatment or monitoring may be recommended. It’s essential to follow up as advised to ensure your skin health remains a priority.
Frequency of Screenings
The frequency of skin cancer screenings can vary based on individual risk factors. Generally, adults should have a full-body skin exam at least once a year, but those with a history of skin cancer or high-risk factors may need more frequent evaluations. Always consult with your healthcare provider to determine the best schedule for you.
In conclusion, understanding the benefits of early detection and knowing what to expect during a screening can significantly impact your skin health journey. Regular screenings are a proactive step towards maintaining your overall well-being. 🌞

Frequently Asked Questions about Skin Cancer Screening
What is Skin Cancer Screening?
Skin cancer screening is a preventive measure that involves examining the skin for signs of cancer. This can include visual inspections by a healthcare professional or self-examinations to identify any unusual moles or skin changes.
Why is Skin Cancer Screening Important?
Early detection of skin cancer can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Regular screenings help identify skin changes that may indicate cancer, allowing for timely intervention.
Who Should Get Screened for Skin Cancer?
Individuals at higher risk, such as those with a family history of skin cancer, fair skin, or a history of excessive sun exposure, should consider regular screenings. It’s also advisable for anyone noticing changes in their skin to seek evaluation.
How Often Should I Get a Skin Cancer Screening?
The frequency of skin cancer screenings can vary based on individual risk factors. Generally, adults should have a professional skin exam at least once a year, while self-exams can be performed monthly.
What Happens During a Skin Cancer Screening?
During a screening, a healthcare provider will examine your skin for any suspicious moles or lesions. They may use a dermatoscope for a closer look. If any areas appear concerning, a biopsy may be recommended.
What Are the Costs Associated with Skin Cancer Screening?
The cost of skin cancer screening can vary widely depending on location, provider, and whether you have insurance. Many insurance plans cover annual skin exams, but it’s best to check with your provider for specifics.
Are There Guidelines for Skin Cancer Screening?
Yes, there are established guidelines for skin cancer screening. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends that adults perform self-exams monthly and have a professional skin exam annually, especially if they have risk factors.
Where Can I Find Skin Cancer Screening Near Me?
You can find local screening options by searching online for skin cancer screening near me or by contacting local dermatology clinics. Many communities also offer free or low-cost screening events.
What Should I Do If I Find a Suspicious Mole?
If you notice a mole that changes in size, shape, or color, or if it itches or bleeds, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional as soon as possible for evaluation.
Can Skin Cancer Be Prevented?
While not all skin cancers can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by practicing sun safety, such as using sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding tanning beds.
What Are the Different Types of Skin Cancer?
The most common types of skin cancer include:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Melanoma
How Can I Prepare for My Skin Cancer Screening?
To prepare for your screening, consider the following:
- Wear loose clothing for easy access to your skin.
- Bring a list of any skin changes you’ve noticed.
- Be ready to discuss your medical history and any risk factors.
What Should I Expect After a Skin Cancer Screening?
After your screening, your healthcare provider will discuss any findings with you. If a biopsy is performed, results typically take a few days to a week. Follow-up appointments may be necessary based on the results.




